In the past few years, the Linux community has been blessed with some remarkable advancements in the area of package management on Linux systems, especially when it comes to universal or cross-distribution software packaging and distribution. One of such advancements is the Snap package format developed by Canonical, the makers of the popular Ubuntu Linux.
What are Snap Packages?
Snaps are cross-distribution, dependency-free, and easy to install applications packaged with all their dependencies to run on all major Linux distributions. From a single build, a snap (application) will run on all supported Linux distributions on desktop, in the cloud, and IoT. Supported distributions include Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, Arch Linux, Manjaro, and CentOS/RHEL.
Snaps are secure – they are confined and sandboxed so that they do not compromise the entire system. They run under different confinement levels (which is the degree of isolation from the base system and each other). More notably, every snap has an interface carefully selected by the snap’s creator, based on the snap’s requirements, to provide access to specific system resources outside of their confinement such as network access, desktop access, and more.
Another important concept in the snap ecosystem is Channels. A channel determines which release of a snap is installed and tracked for updates and it consists of and is subdivided by, tracks, risk-levels, and branches.
The main components of the snap package management system are:
- snapd – the background service that manages and maintains your snaps on a Linux system.
- snap – both the application package format and the command-line interface tool used to install and remove snaps and do many other things in the snap ecosystem.
- snapcraft – the framework and powerful command-line tool for building snaps.
- snap store – a place where developers can share their snaps and Linux users search and install them.
Besides, snaps also update automatically. You can configure when and how updates occur. By default, the snapd daemon checks for updates up to four times a day: each update check is called a refresh. You can also manually initiate a refresh.
How to Install Snapd in Linux
As described above, the snapd daemon is the background service that manages and maintains your snap environment on a Linux system, by implementing the confinement policies and controlling the interfaces that allow snaps to access specific system resources. It also provides the snap command and serves many other purposes.
To install the snapd package on your system, run the appropriate command for your Linux distribution.
------------ [On Debian and Ubuntu] ------------ $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install snapd ------------ [On Fedora Linux] ------------ # dnf install snapd ------------ [On CentOS and RHEL] ------------ # yum install epel-release # yum install snapd ------------ [On openSUSE - replace openSUSE_Leap_15.0 with the version] ------------ $ sudo zypper addrepo --refresh https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/system:/snappy/openSUSE_Leap_15.0 snappy $ sudo zypper --gpg-auto-import-keys refresh $ sudo zypper dup --from snappy $ sudo zypper install snapd ------------ [On Manjaro Linux] ------------ # pacman -S snapd ------------ [On Arch Linux] ------------ # git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/snapd.git # cd snapd # makepkg -si
After installing snapd on your system, enable the systemd unit that manages the main snap communication socket, using the systemctl commands as follows.
On Ubuntu and its derivatives, this should be triggered automatically by the package installer.
$ sudo systemctl enable --now snapd.socket
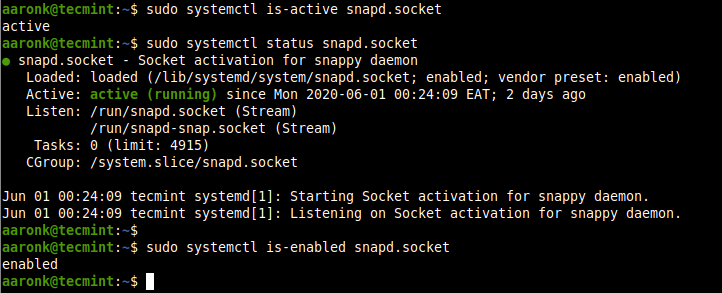
Note that you can’t run the snap command if the snapd.socket is not running. Run the following commands to check if it is active and is enabled to automatically start at system boot.
$ sudo systemctl is-active snapd.socket $ sudo systemctl status snapd.socket $ sudo systemctl is-enabled snapd.socket
Next, enable classic snap support by creating a symbolic link between /var/lib/snapd/snap and /snap as follows.
$ sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snap
To check the version of snapd and snap command-line tool installed on your system, run the following command.
$ snap version
How to Install Snaps in Linux
The snap command allows you to install, configure, refresh and remove snaps, and interact with the larger snap ecosystem.
Before installing a snap, you can check if it exists in the snap store. For example, if the application belongs in the category of “chat servers” or “media players“, you can run these commands to search for it, which will query the store for available packages in the stable channel.
$ snap find "chat servers" $ snap find "media players"
To show detailed information about a snap, for example, rocketchat-server, you can specify its name or path. Note that names are looked for both in the snap store and in the installed snaps.
$ snap info rocketchat-server
To install a snap on your system, for example, rocketchat-server, run the following command. If no options are provided, a snap is installed tracking the “stable” channel, with strict security confinement.
$ sudo snap install rocketchat-server
You can opt to install from a different channel: edge, beta, or candidate, for one reason or the other, using the --edge, --beta, or --candidate options respectively. Or use the --channel option and specify the channel you wish to install from.
$ sudo snap install --edge rocketchat-server $ sudo snap install --beta rocketchat-server $ sudo snap install --candidate rocketchat-server
Manage Snaps in Linux
In this section, we will learn how to manage snaps in Linux system.
Viewing Installed Snaps
To display a summary of snaps installed on your system, use the following command.
$ snap list
To list the current revision of a snap being used, specify its name. You can also list all its available revisions by adding the --all option.
$ snap list mailspring OR $ snap list --all mailspring
Updating and Reverting Snaps
You can update a specified snap, or all snaps in the system if none are specified as follows. The refresh command checks the channel being tracked by the snap and it downloads and installs a newer version of the snap if it is available.
$ sudo snap refresh mailspring OR $ sudo snap refresh #update all snaps on the local system
After updating an app to a new version, you can revert to a previously used version using the revert command. Note that the data associated with the software will also be reverted.
$ sudo snap revert mailspring
Now when you check all revisions of mailspring, the latest revision is disabled, a previously used revision is now active.
$ snap list --all mailspring
Disabling/Enabling and Removing Snaps
You can disable a snap if you do not want to use it. When disabled, a snap’s binaries and services will no longer be available, however, all the data will still be there.
$ sudo snap disable mailspring
If you need to use the snap again, you can enable it back.
$ sudo snap enable mailspring
To completely remove a snap from your system, use the remove command. By default, all of a snap’s revisions are removed.
$ sudo snap remove mailspring
To remove a specific revision, use the --revision option as follows.
$ sudo snap remove --revision=482 mailspring
It is key to note that when you remove a snap, its data (such as internal user, system, and configuration data) is saved by snapd (version 2.39 and higher) as a snapshot, and stored on the system for 31 days. In case you reinstall the snap within the 31 days, you can restore the data.
Conclusion
Snaps are becoming more popular within the Linux community as they provide an easy way to install software on any Linux distribution. In this guide, we have shown how to install and work with snaps in Linux. We covered how to install snapd, install snaps, view installed snaps, update and revert snaps, and disable/enable and remove snaps.
You can ask questions or reach us via the feedback form below. In the next part of this guide, we will cover managing snaps (commands, aliases, services, and snapshots) in Linux.