In this series of articles, we are going to cover the entire Cloudera Hadoop Cluster Building building with Vendor and Industrial recommended best practices.
OS installation and doing OS level Pre-requisites are the first steps to build a Hadoop Cluster. Hadoop can run on the various flavor of Linux platform: CentOS, RedHat, Ubuntu, Debian, SUSE etc., In real-time production, most of the Hadoop Clusters are built on top of RHEL/CentOS, we will use CentOS 7 for demonstration in this series of tutorials.
In an Organization, OS installation can be done using kickstart. If it is a 3 to 4 node cluster, manual installation is possible but if we build a big cluster with more than 10 nodes, it’s tedious to install OS one by one. In this scenario, the Kickstart method comes into the picture, we can proceed with the mass installation using kickstart.
Achieving good performance from a Hadoop Environment is depends on provisioning the correct Hardware & Software. So, building a production Hadoop cluster involves a lot of consideration regarding Hardware and Software.
In this article, we will go through various Benchmarks about OS installation and some best practices for deploying Cloudera Hadoop Cluster Server on CentOS/RHEL 7.
Important Consideration and Best Practices for Deploying Hadoop Server
The following are the best practices for setting up deploying Cloudera Hadoop Cluster Server on CentOS/RHEL 7.
- Hadoop servers do not require enterprise standard servers to build a cluster, it requires commodity hardware.
- In the production cluster, having 8 to 12 data disks are recommended. According to the nature of the workload, we need to decide on this. If the cluster is for compute-intensive applications, having 4 to 6 drives is best practice to avoid I/O issues.
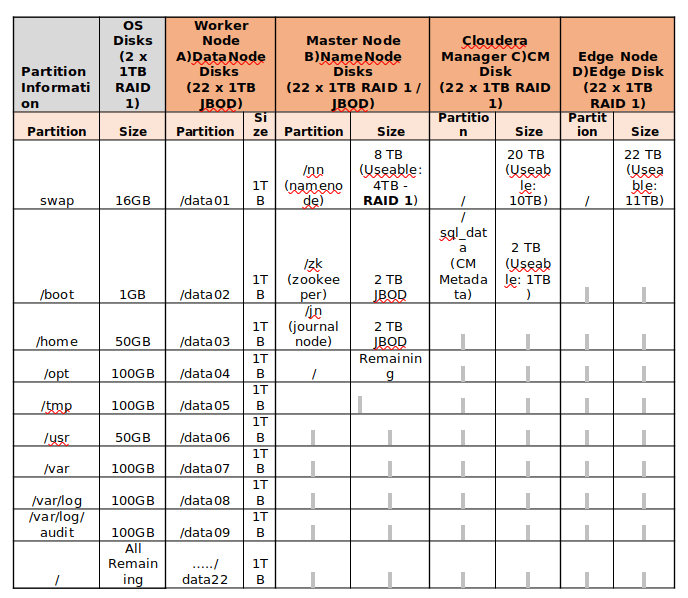
- Data drives should be partitioned individually, for example – starting from /data01 to /data10.
- RAID configuration is not recommended for worker nodes, because Hadoop itself providing fault-tolerance on data by replicating the blocks into 3 by default. So JBOD is best for worker nodes.
- For Master Servers, RAID 1 is the best practice.
- The default filesystem on CentOS/RHEL 7.x is XFS. Hadoop supports XFS, ext3, and ext4. The recommended file-system is ext3 as it is tested for good performance.
- All the servers should be having the same OS version, at-least same minor release.
- It is best practice to have homogeneous hardware (all worker nodes should have the same hardware characteristics (RAM, disk space & Core etc).
- According to the cluster workload (Balanced Workload, Compute Intensive, I/O Intensive) and size, resource (RAM, CPU) planning per server will get differ.
Find the below Example for Disk Partitioning of the servers of 24TB storage.
Installing CentOS 7 for Hadoop Server Deployment
Things you need to know before installing CentOS 7 server for Hadoop Server.
- Minimal installation is enough for Hadoop Servers (worker nodes), in some cases, GUI can be installed only for Master servers or Management servers where we can use browsers for Web UIs of Management tools.
- Configuring networks, hostname, and other OS-related settings can be done after OS installation.
- In real-time, server vendors will be having their own console to interact and manage the servers, for example – Dell servers are having iDRAC which is a device, embedded with servers. Using that iDRAC interface we can install OS with having an OS image in our local system.
In this article, we have installed OS (CentOS 7) in VMware virtual machine. Here, we will not be having multiple disks to perform partitions. CentOS is similar to RHEL (same functionality), so we will see the steps to install CentOS.
1. Begin by downloading the CentOS 7.x ISO image in your local windows system and select it while booting the virtual machine. Select ‘Install CentOS 7‘ as shown.
2. Select the Language, default will be English, and click continue.
3. Software Selection – Select the ‘Minimal Installation‘ and click ‘Done‘.

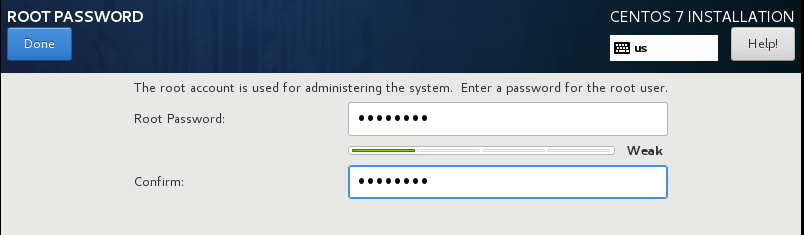
4. Set the root password as it will prompt us to set.
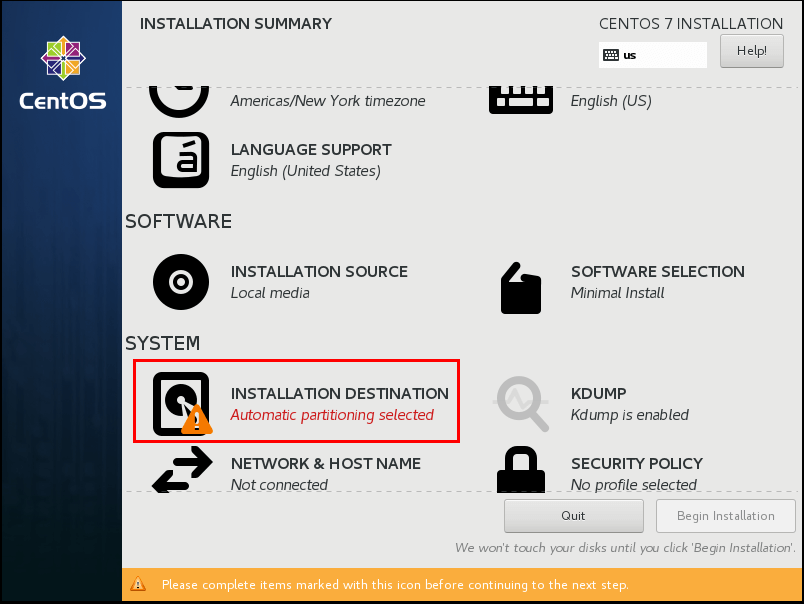
5. Installation Destination – This is the important step to be cautious. We need to select the disk where the OS has to be installed, dedicated disk should be selected for OS. Click the ‘Installation Destination‘ and select the Disk, in real-time multiple disks will be there, we need to select, preferable ‘sda‘.
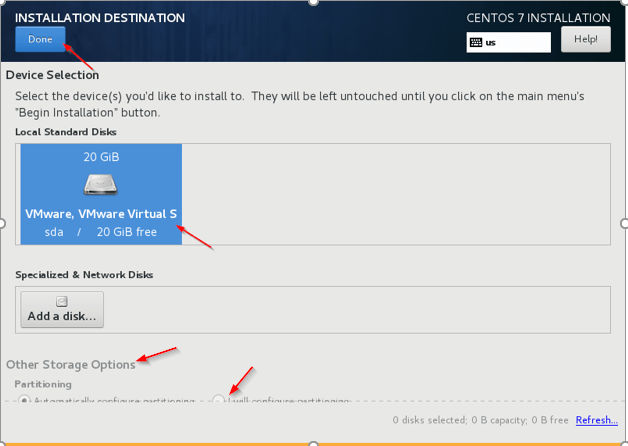
6. Other Storage Options – Choose the second option (I will configure partitioning) to configure OS related partitioning like /var, /var/log, /home, /tmp, /opt, /swap.

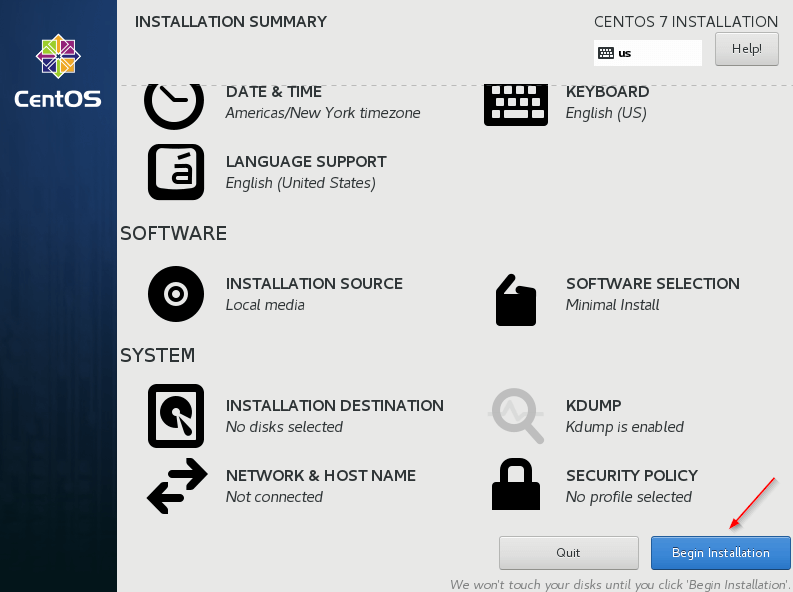
7. Once done, begin the installation.
8. Once the Installation completed, reboot the server.
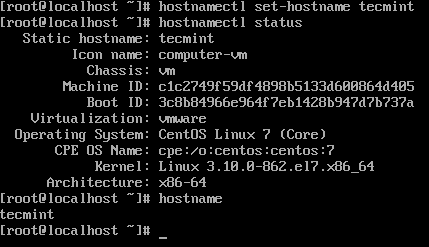
9. Login into the server and set the hostname.
# hostnamectl status # hostnamectl set-hostname tecmint # hostnamectl status
Summary
In this article, we have gone through OS installation steps and best practices for filesystem partitioning. These are all general guideline, according to the nature of the workload, we may need to concentrate on more nuances to achieve the best performance of the cluster. Cluster planning is art for the Hadoop administrator. We will have deep dive into OS level pre-requisites and security Hardening in the next article.
