Android (x86) is a project which aims to port the Android system to Intel x86 processors to let users install it easily on any computer, the way they do this is by taking an android source code, patching it to work on Intel x86 processors and some laptops and tablets.
In this article, you will learn how to install the latest version of Android OS on your VirtualBox platform on Linux. If you want, you can also install Android directly on your Linux, Windows or Mac system.
Step 1: Install VirtualBox in Linux
1. VirtualBox is available to install easily via official repositories in most Linux distributions, to install it on Debian-based Linux distributions run the following commands.
First, add the following line to your /etc/apt/sources.list file and according to your distribution release, make sure to replace '<mydist>' with your distribution release.
deb [arch=amd64] https://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian <mydist> contrib
Then import public key and install VirtualBox as shown.
$ wget -q https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox_2016.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add - $ wget -q https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add - $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install virtualbox-6.1
For other Linux distributions like RHEL, CentOS, and Fedora, use the following article to install Virtualbox.
Step 2: Download and Install Android in Virtualbox
2. This is an easy step, go to the Android-x86 project and grab the latest Android version of Android-x86 64-bit ISO file for your architecture.
3. To install Android on VirtualBox, you need first to boot from the .iso image that you downloaded, to do so, open VirtualBox, Click on new to create a new virtual machine, and choose the settings as follows.
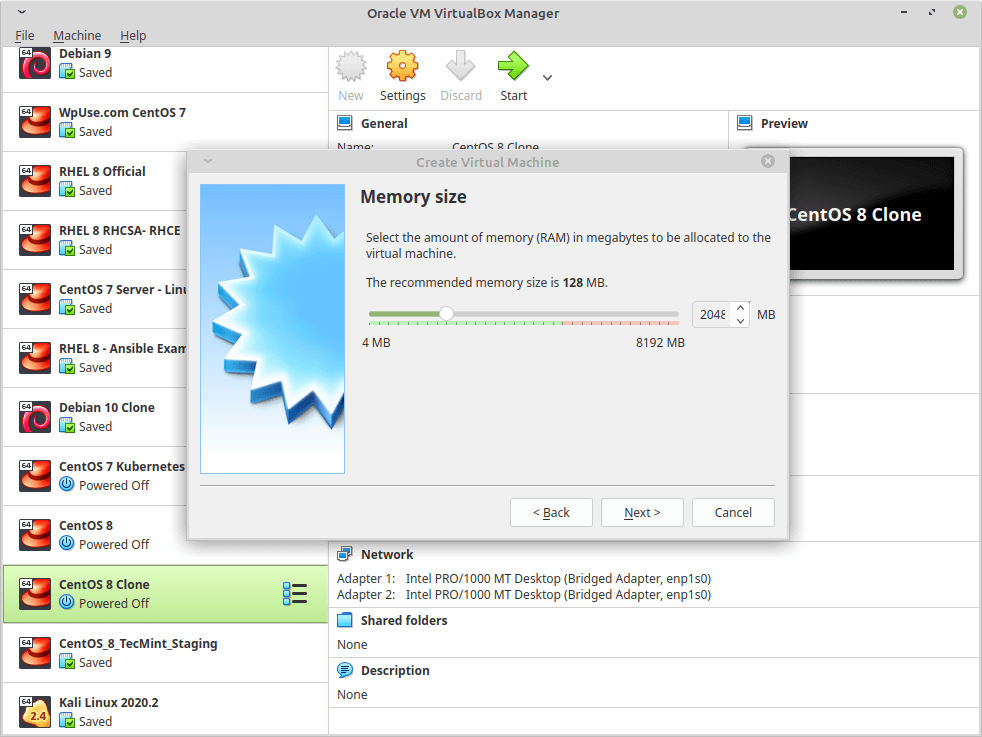
4. Then it will ask you to choose a Memory size for the machine, Android needs 1GB of RAM to work perfectly, but I will choose 2GB since I only have 4GB of RAM on my computer.
5. Now select “Create a virtual hard drive now” to create a new one.

6. It will now ask you for the type of the new virtual hard drive, select VDI.
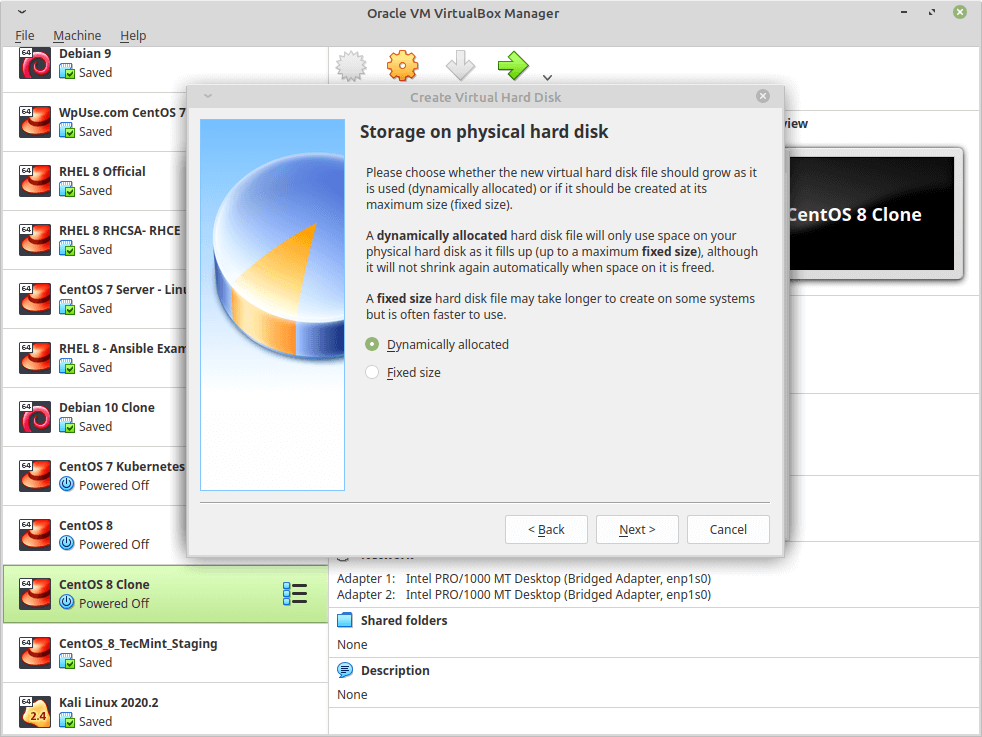
7. Now choose the size of the virtual hard drive, you may choose any size you want, no less than 10GB so the system can be installed correctly beside any future apps that you want to install.
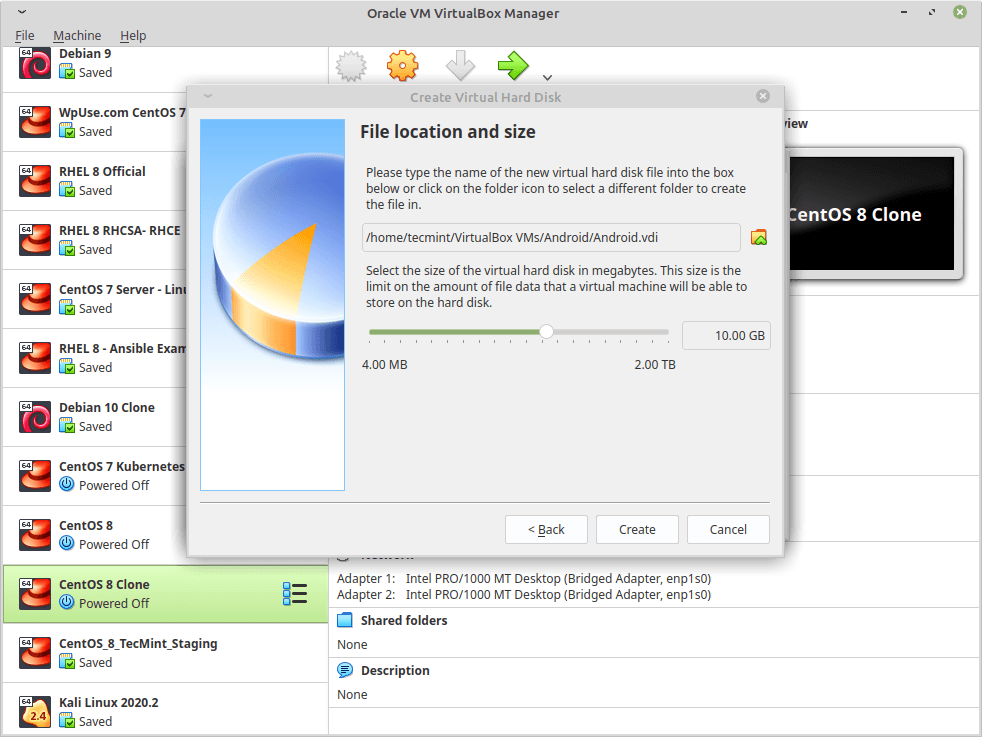
8. Now that’s your first virtual machine is created, now to boot from the .iso file that you downloaded, select the virtual machine from the list on the left, click on Settings, and go for “storage”, do as follow, and select the .iso image of Android.
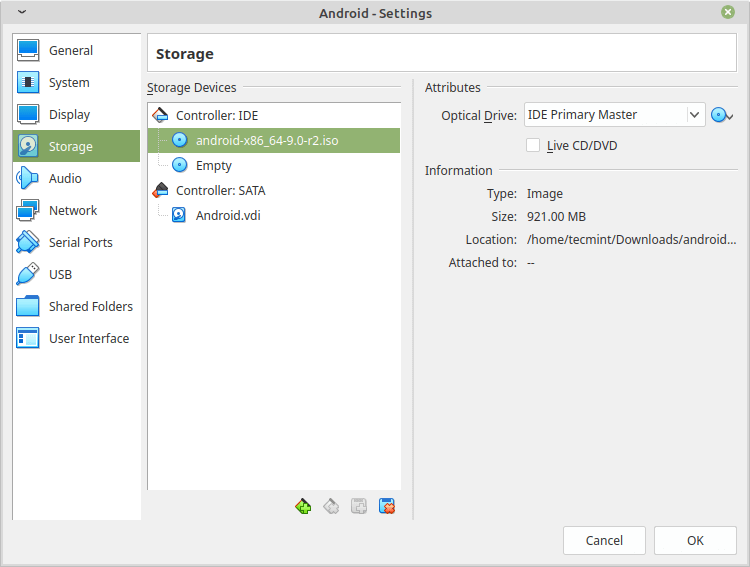
9. Click on OK, and start the machine to boot the .iso image, choose “Installation” to start installing the system on the virtual machine.

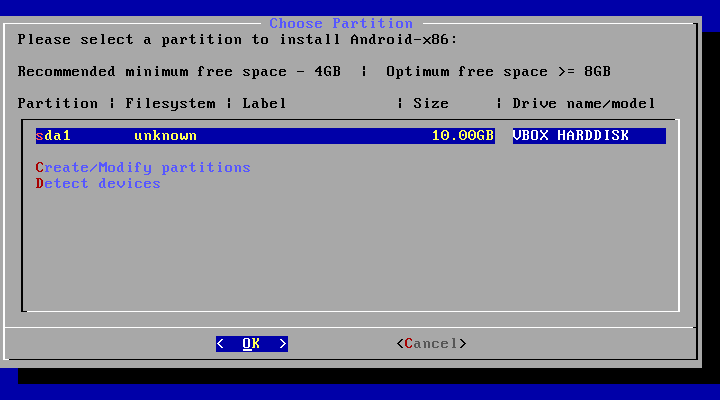
10. Please select a partition to install Android-x86.
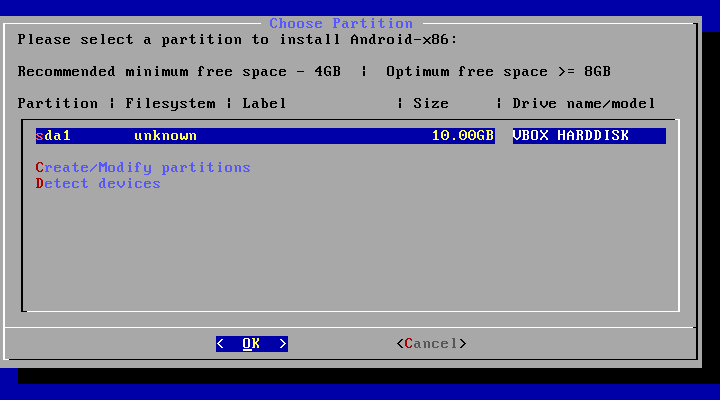
11. Now you will be prompted cfdisk which is a partitioning tool that we will use to create a new hard drive, so we can install android on it, click on “New”.
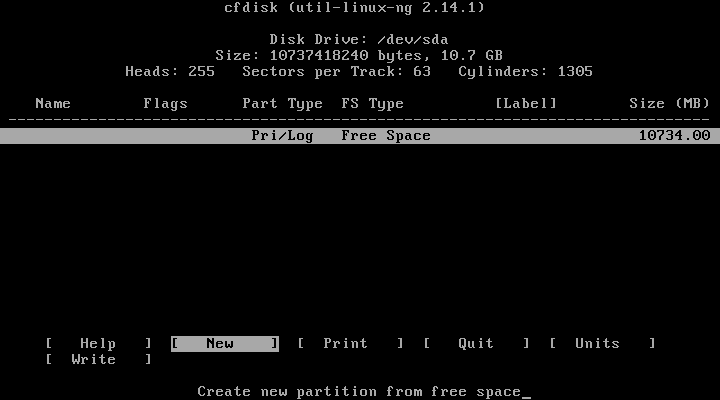
12. Choose “Primary” as partition type.
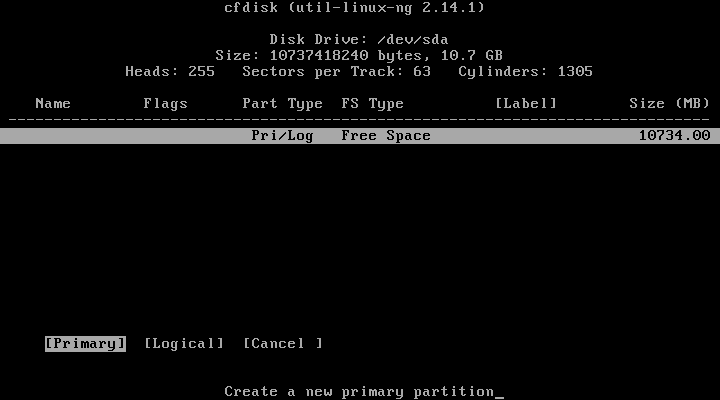
13. Next, select the size of the partition.

14. Now, we have to make the new hard drive bootable in order to be able to write changes to the disk, click on “Bootable” to give the bootable flag to the new partition, you won’t notice any changes in fact but the bootable flag will be given to that partition.
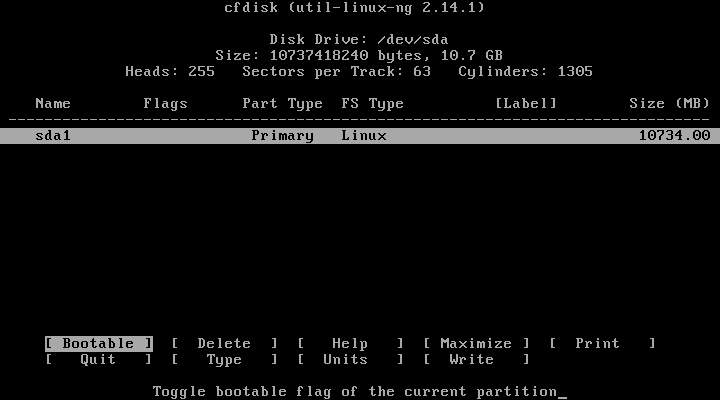
15. After that, click on “Write” to write the changes to the hard drive.
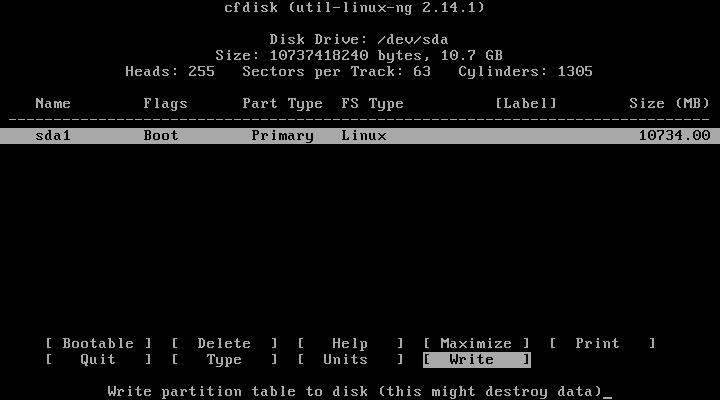
16. It will ask you if you are sure, write “yes”, and click on Enter.
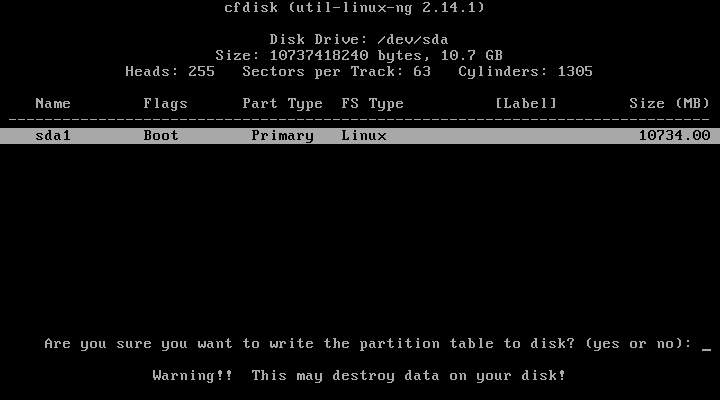
17. Now that’s our new hard drive is created, now click on Quit and you will see something like this, select the partition that you created before in order to install android on it and hit Enter.
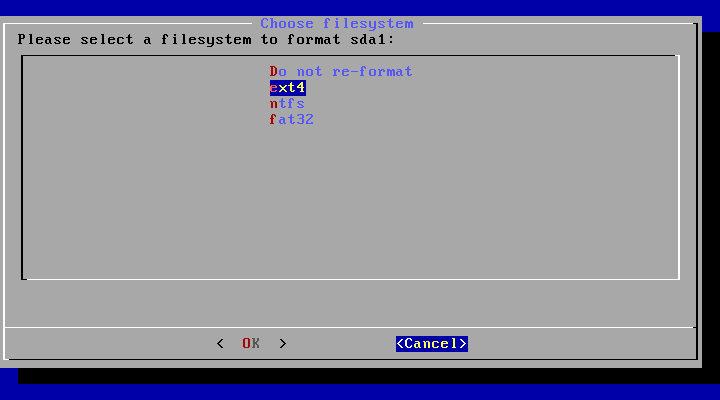
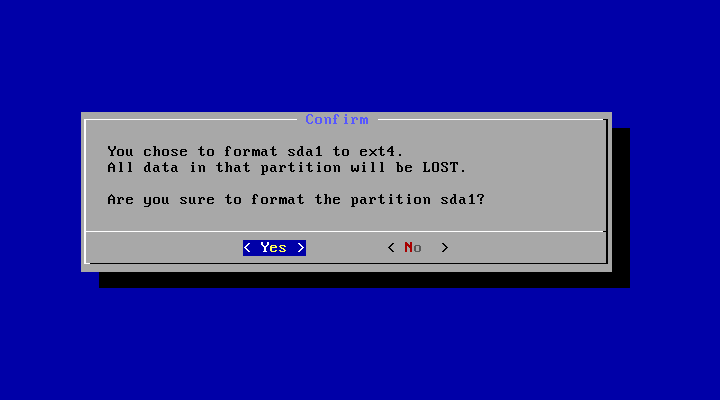
18. Choose “ext4” as a filesystem for the hard drive and format.
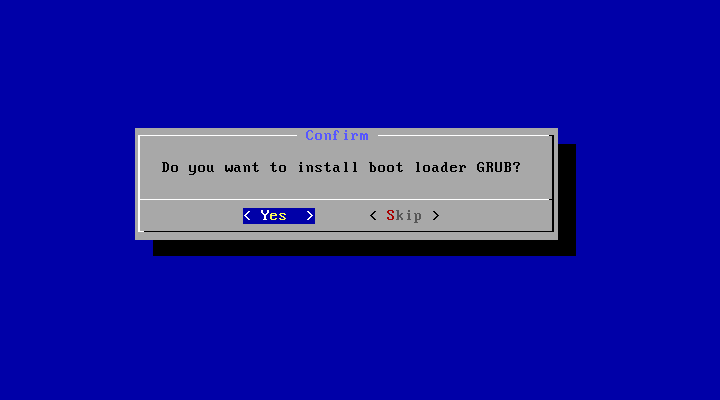
19. You will be asked now if you want to install GRUB bootloader, of course, you will select Yes because if you don’t, you won’t be able to boot the new system, so choose “Yes” and hit Enter.
20. Finally, you will be asked if you want to make the /system partition writeable, choose Yes, it will help in a lot of things later after you install the system.
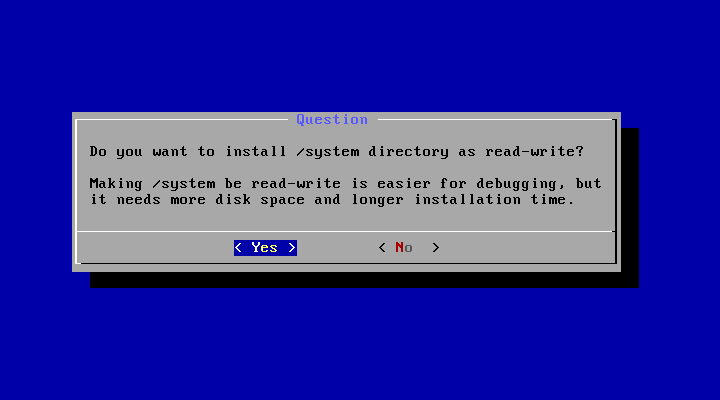
21. The installer will start the installation process after the installer finishes the job, choose Reboot.
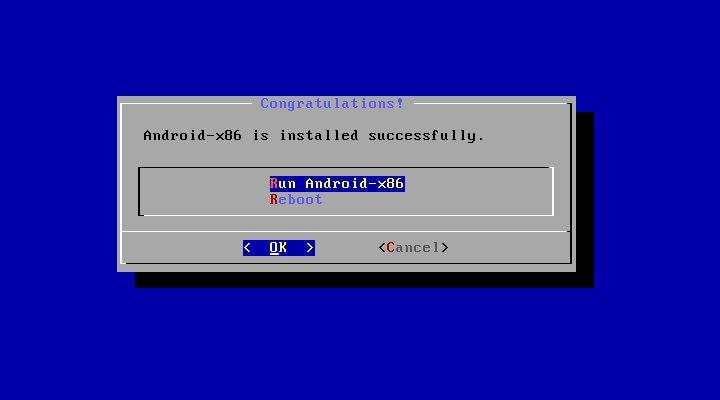
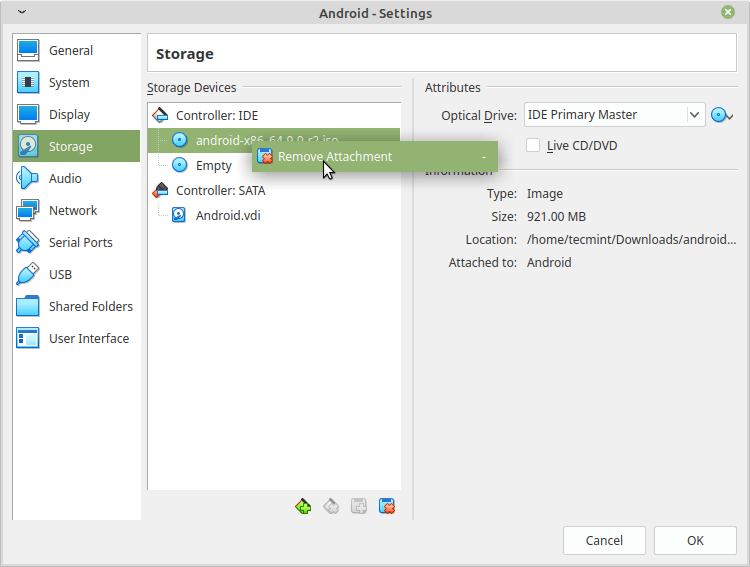
22. Now that’s we installed Android on our hard drive, the problem is now that VirtualBox will keep loading the .iso image file instead of booting from the virtual hard drive, so to fix this problem, go to Settings, under “storage” select the .iso file and remove it from the booting menu.
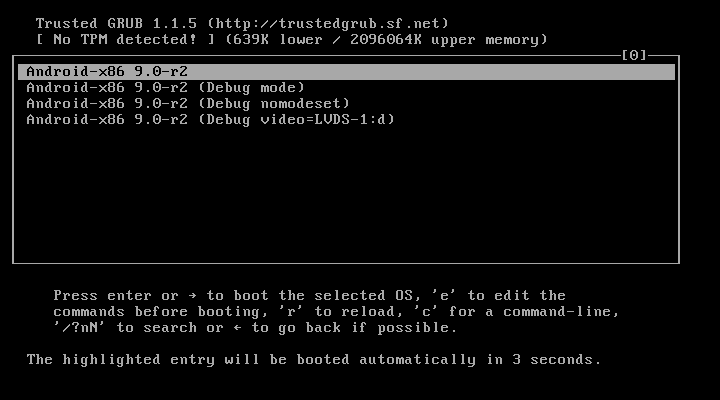
23. Now you can start the virtual machine with the installed android system.

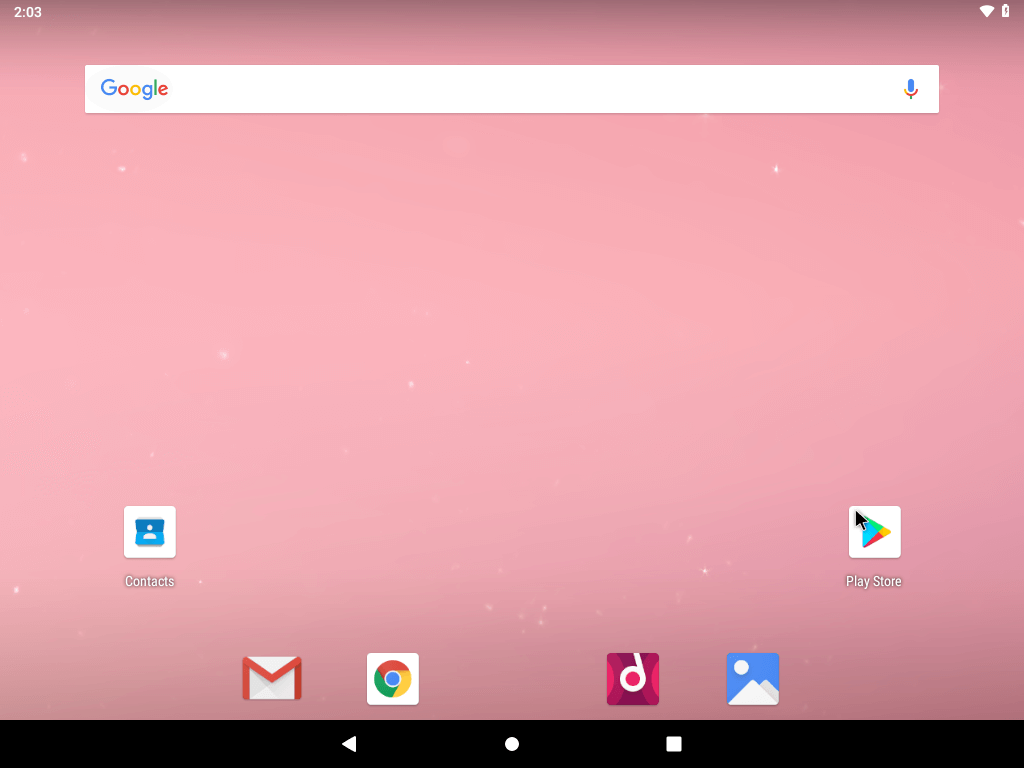
Installing Android x86 will be good for you if you don’t have a smartphone and you want to use the Play Store apps easily, have you ever tried to install android x86? What were the results? Do you think that android may become a “real operation system” targeting PCs in the feature?
