Apache NIFI is an open-source scalable tool to manage transformation, data routing, and system mediation logic. To put it in layman’s terms nifi simply automates the flow of data between two or more systems.
It is cross-platform and written in Java that supports 180+ plugins that allow you to interact with different kinds of systems. In this article, we will take a look at how to set up Nifi on Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 18.04.
Java is mandatory for nifi to work. By default, Ubuntu comes with OpenJDK 11. To check the java version run the following command.
$ java -version

If your distribution does not have java installed take a look at our comprehensive article on how to install Java on Ubuntu.
Installing on Apache Nifi in Ubuntu
To install nifi on Ubuntu, you need to download the Nifi tar file or use the wget command from the terminal to download the file. The file size is around 1.5GB so it will take some time to complete the download depending upon your Internet speed.
$ wget https://apachemirror.wuchna.com/nifi/1.13.2/nifi-1.13.2-bin.tar.gz
Now extract the tar file to whatever location you want.
$ sudo tar -xvzf nifi-1.13.2-bin.tar.gz
Now you can go into the bin directory under the extracted directory and start the nifi process.
$ sudo ./nifi.sh start
Alternatively, you can create a soft link and change the source directory where you placed your nifi files.
$ sudo ln -s /home/karthick/Downloads/nifi-1.13.2/bin/nifi.sh /usr/bin/nifi
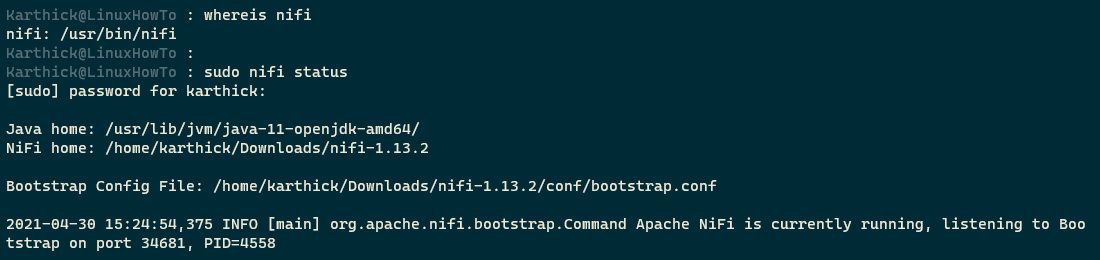
Run the below command to check if softlink works fine. In my case, it is working fine.
$ whereis nifi $ sudo nifi status
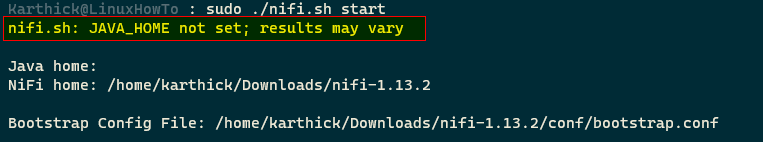
You may encounter the below warning if you have not set up the Java home properly.
You can suppress this warning by adding Java home in nifi-env.sh file present in the same bin directory.
$ sudo nano nifi-env.sh
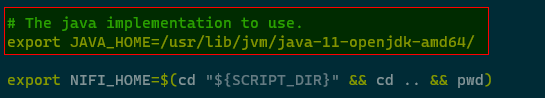
Add Java_Home path as shown.
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/
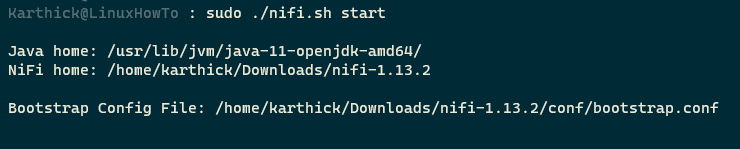
Now try starting nifi and you will not see any warning.
$ sudo ./nifi.sh start
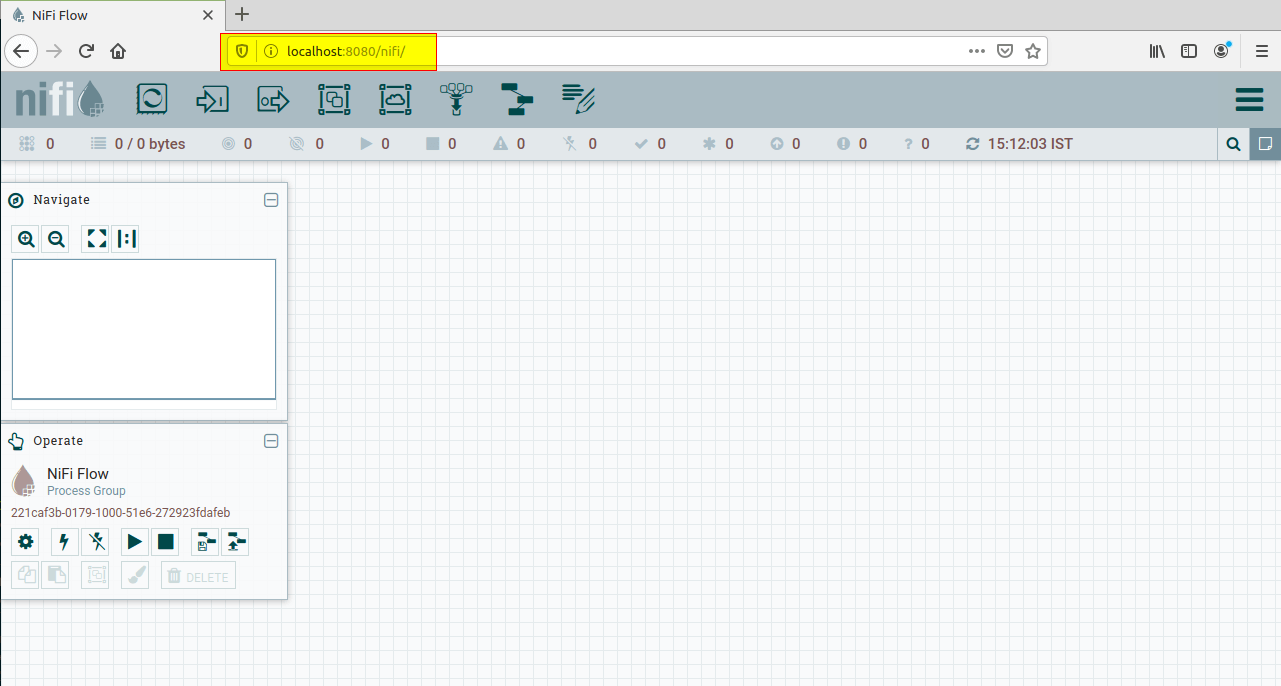
Nifi is a web-based tool so you can choose your favorite browser and type the following URL to connect to Nifi.
$ localhost:8080/nifi
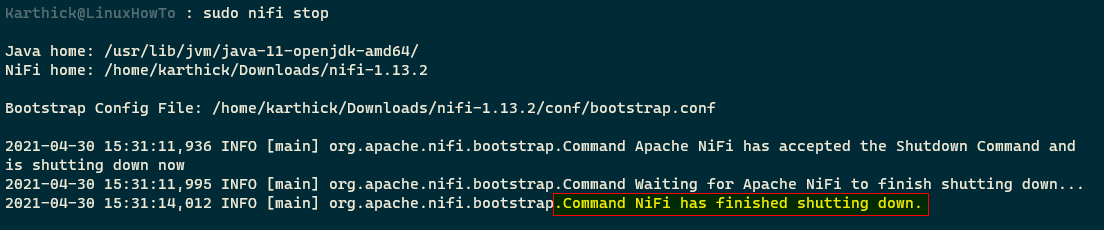
To stop the nifi process run the following command.
$ sudo nifi stop → Soft link $ sudo nifi.sh stop → From bin directory
That’s it for this article. Please use the comment section to share the feedback. We would love to hear from you.
