PHP (recursive acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is an open-source, popular general-purpose scripting language that is widely-used and best suited for developing websites and web-based applications. It is a server-side scripting language that can be embedded in HTML.
Currently, there are three supported versions of PHP, i.e PHP 5.6, 7.0, and 8.0. Meaning PHP 5.3, 5.4, and 5.5 have all reached the end of life; they are no longer supported with security updates.
In this article, we will explain how to install all the supported versions of PHP in Ubuntu and its derivatives with the most requested PHP extensions for both Apache and Nginx web servers using an Ondřej Surý PPA. We will also explain how to set the default version of PHP to be used on the Ubuntu system.
Note that PHP 7.x is the supported stable version in the Ubuntu software repositories, you can confirm this by running the apt command below.
$ sudo apt show php OR $ sudo apt show php -a
Package: php Version: 1:7.0+35ubuntu6 Priority: optional Section: php Source: php-defaults (35ubuntu6) Origin: Ubuntu Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <[email protected]> Original-Maintainer: Debian PHP Maintainers <[email protected]> Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug Installed-Size: 11.3 kB Depends: php7.0 Supported: 5y Download-Size: 2,832 B APT-Sources: http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages Description: server-side, HTML-embedded scripting language (default) PHP (recursive acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely-used open source general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and can be embedded into HTML. . This package is a dependency package, which depends on Debian's default PHP version (currently 7.0).
To install the default PHP version from the Ubuntu software repositories, use the command below.
$ sudo apt install php
Install PHP (5.6, 7.x, 8.0) on Ubuntu Using PPA
1. First start by adding Ondřej Surý PPA to install different versions of PHP – PHP 5.6, PHP 7.x, and PHP 8.0 on the Ubuntu system.
$ sudo apt install python-software-properties $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
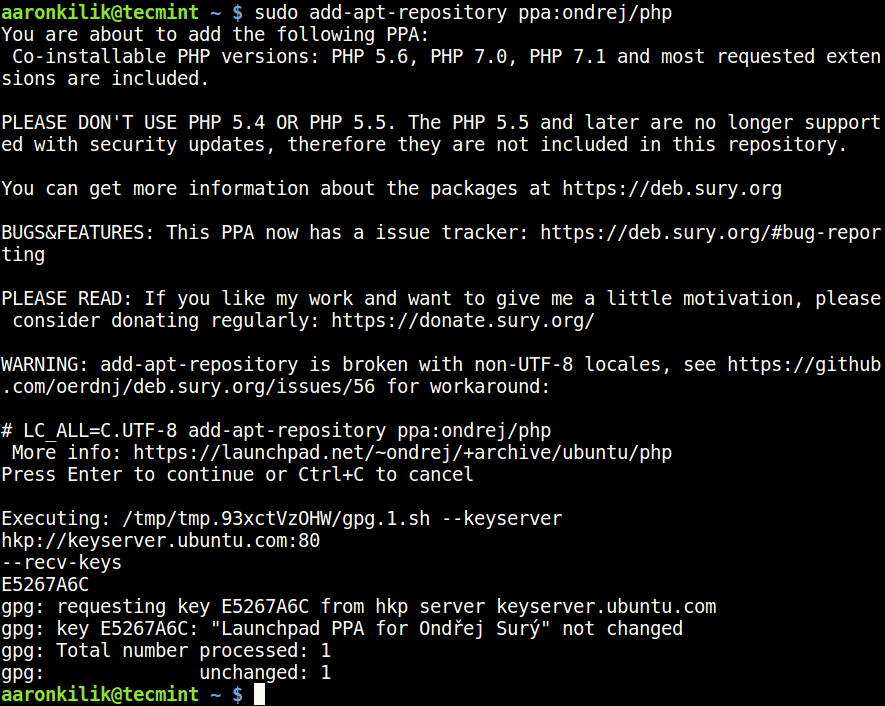
2. Next, update the system as follows.
$ sudo apt-get update
3. Now install different supported versions of PHP as follows.
For Apache Web Server
$ sudo apt install php5.6 [PHP 5.6] $ sudo apt install php7.0 [PHP 7.0] $ sudo apt install php7.1 [PHP 7.1] $ sudo apt install php7.2 [PHP 7.2] $ sudo apt install php7.3 [PHP 7.3] $ sudo apt install php7.4 [PHP 7.4] $ sudo apt install php8.0 [PHP 8.0]
For Nginx Web Server
$ sudo apt install php5.6-fpm [PHP 5.6] $ sudo apt install php7.0-fpm [PHP 7.0] $ sudo apt install php7.1-fpm [PHP 7.1] $ sudo apt install php7.2-fpm [PHP 7.2] $ sudo apt install php7.3-fpm [PHP 7.3] $ sudo apt install php7.4-fpm [PHP 7.4] $ sudo apt install php8.0-fpm [PHP 8.0]
4. To install any PHP modules, simply specify the PHP version and use the auto-completion functionality to view all modules as follows.
------------ press Tab key for auto-completion ------------ $ sudo apt install php5.6 $ sudo apt install php7.0 $ sudo apt install php7.1 $ sudo apt install php7.2 $ sudo apt install php7.3 $ sudo apt install php7.4 $ sudo apt install php8.0
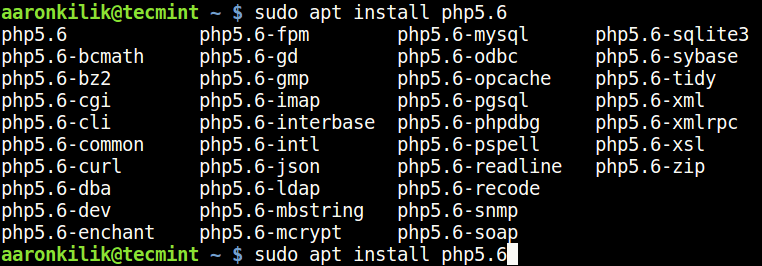
5. Now you can install most required PHP modules from the list.
------------ Install PHP Modules ------------ $ sudo apt install php5.6-cli php5.6-xml php5.6-mysql $ sudo apt install php7.0-cli php7.0-xml php7.0-mysql $ sudo apt install php7.1-cli php7.1-xml php7.1-mysql $ sudo apt install php7.2-cli php7.2-xml php7.2-mysql $ sudo apt install php7.3-cli php7.3-xml php7.3-mysql $ sudo apt install php7.3-cli php7.4-xml php7.4-mysql $ sudo apt install php7.3-cli php8.0-xml php8.0-mysql
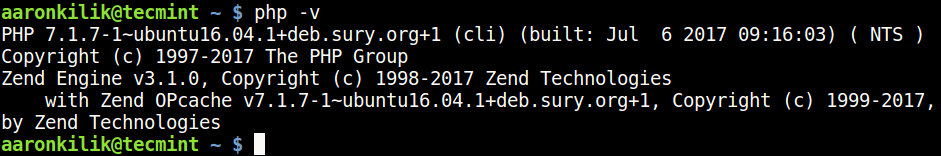
6. Finally, verify your default PHP version used on your system like this.
$ php -v
Set Default PHP Version in Ubuntu
7. You can set the default PHP version to be used on the system with the update-alternatives command, after setting it, check the PHP version to confirm as follows.
------------ Set Default PHP Version 5.6 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php5.6
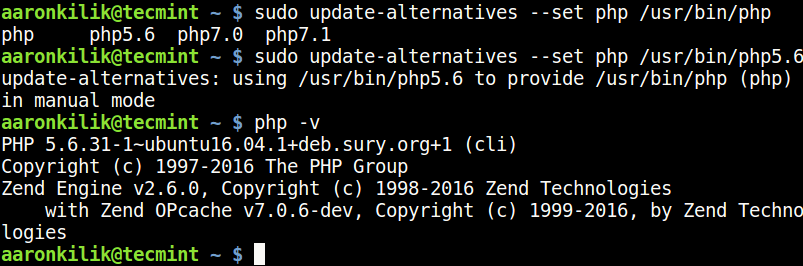
------------ Set Default PHP Version 7.0 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.0
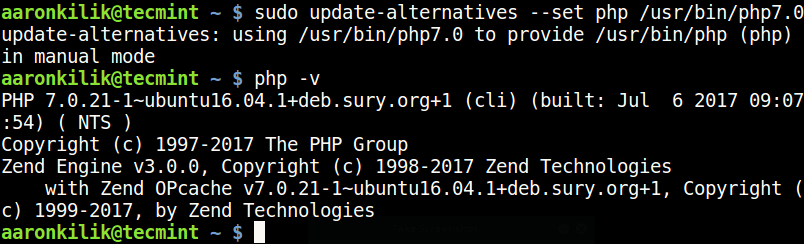
------------ Set Default PHP Version 7.1 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.1
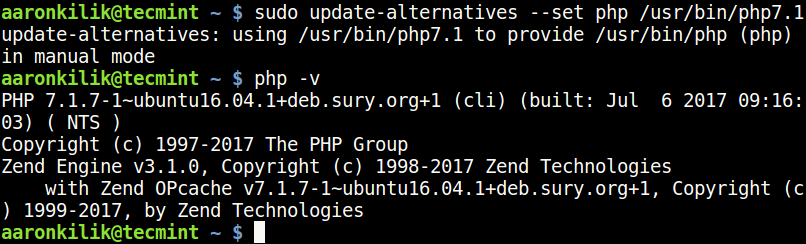
------------ Set Default PHP Version 8.0 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php8.0
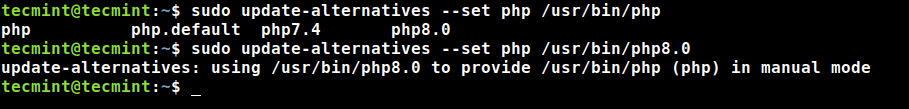
8. To set the PHP version that will work with the Apache web server, use the commands below. First, disable the current version with the a2dismod command and then enable the one you want with the a2enmod command.
----------- Disable PHP Version ----------- $ sudo a2dismod php5.6 $ sudo a2dismod php7.0 $ sudo a2dismod php7.1 $ sudo a2dismod php7.2 $ sudo a2dismod php7.3 $ sudo a2dismod php7.4 $ sudo a2dismod php8.0 ----------- Enable PHP Version ----------- $ sudo a2enmod php5.6 $ sudo a2enmod php7.1 $ sudo a2enmod php7.2 $ sudo a2enmod php7.3 $ sudo a2enmod php7.4 $ sudo a2enmod php8.0 ----------- Restart Apache Server ----------- $ sudo systemctl restart apache2
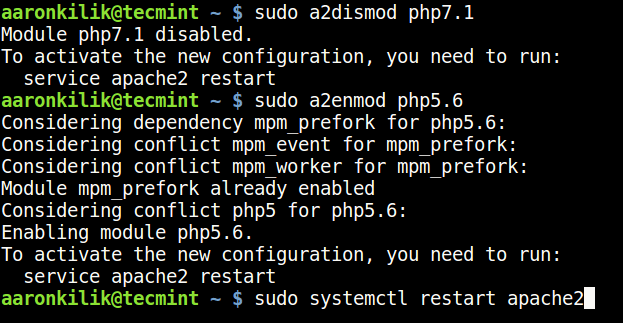
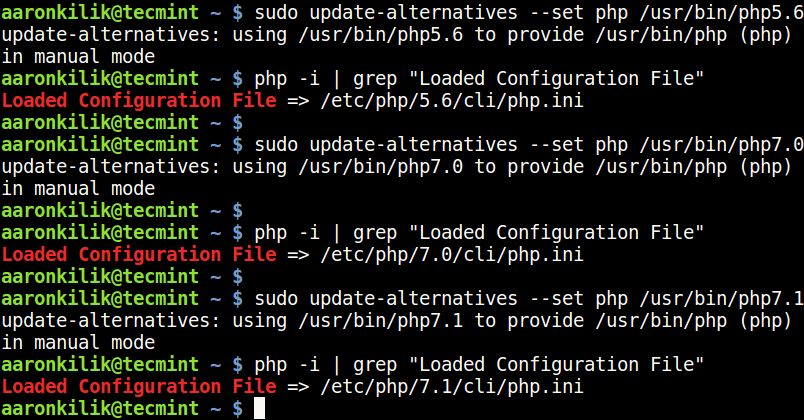
9. After switching from one version to another, you can find your PHP configuration file, by running the command below.
------------ For PHP 5.6 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php5.6 $ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File" ------------ For PHP 7.0 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.0 $ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File" ------------ For PHP 7.1 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.1 $ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File" ------------ For PHP 7.2 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.2 $ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File" ------------ For PHP 7.3 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.3 $ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File" ------------ For PHP 7.4 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php7.4 $ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File" ------------ For PHP 8.0 ------------ $ sudo update-alternatives --set php /usr/bin/php8.0 $ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File"
You may also like:
- How to Use and Execute PHP Codes in Linux Command Line
- 12 Useful PHP Commandline Usage Every Linux User Must Know
- How to Hide PHP Version in HTTP Header
In this article, we showed how to install all the supported versions of PHP in Ubuntu and its derivatives. If you have any queries or thoughts to share, do so via the feedback form below.
