Two commonly used open-source Python web frameworks are Django and Flask. Django is a robust Python framework that allows users to rapidly develop and deploy their web applications by providing an MVC framework that aims at simplifying web app development with less code along with reusable components.
Meanwhile, Flask is a microframework that is lean and devoid of extra libraries or tools. It is minimalistic as it ships with only the basic tools to help you get off the ground with developing your applications.
Without much further ado, let’s jump right in and install the flask on Ubuntu 20.04.
Installing Flask in Ubuntu
1. To install flask on Ubuntu 20.04 using apt package manager, here are the steps to follow:
First, ensure that your system is updated as shown.
$ sudo apt update -y
Once the update is complete, head over to the next step.
2. Next, you will need to install pip alongside other Python dependencies which will enable you to create a virtual environment. It’s in the virtual environment that we are going to install flask.
In case you are wondering why we are not installing Python first, well, Ubuntu 20.04 already comes pre-packaged with Python 3.8, and so there’s no need to install it.
To confirm the presence of Python on Ubuntu 20.04 run:
$ python3 --version

Next, install pip3 and other Python tools as shown.
$ sudo apt install build-essential python3-pip libffi-dev python3-dev python3-setuptools libssl-dev
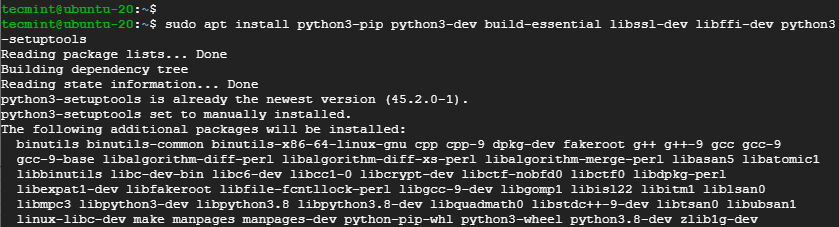
3. Thereafter, install a virtual environment that is going to isolate and run flask in a sandboxed environment.
$ sudo apt install python3-venv

4. Now, create the flask directory and navigate into it.
$ mkdir flask_dir && cd flask_dir
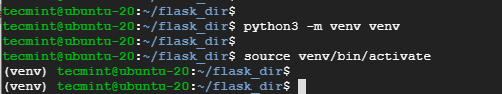
5. Create a virtual environment using Python as follows.
$ python3 -m venv venv
6. Then activate it so that you can install the flask.
$ source venv/bin/activate
Notice how the prompt changes to (venv) to indicate that we are now working inside the virtual environment.
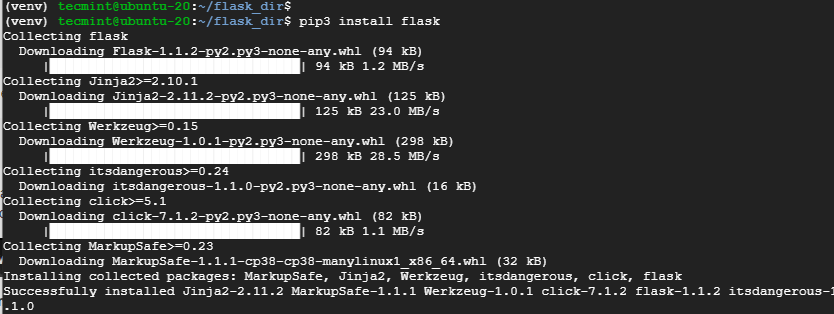
7. Lastly, install flask web framework using pip, which will install all the components of flask including Jinja2, werkzeug WSG web application library & its modules.
$ pip3 install flask
8. To confirm that flask is installed, run:
$ flask --version
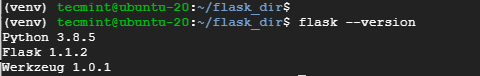
Perfect! Flask is now installed on Ubuntu 20.04. You can now proceed to create and deploy your Python applications using flask.
