Jenkins is a leading self-contained open-source automation server that is used to automate repetitive technical assignments involved in building, testing, and delivering or deploying software.
Jenkins is Java-based and can be installed through Ubuntu packages, Docker, or by downloading and running its web application archive (WAR) file that includes all the contents of a web application to run on a server.
In this article, you will learn how to use the Debian package repository to install Jenkins on Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 18.04 with the apt package manager.
Prerequisites
- Minimum 1 GB of RAM for a small team and 4 GB+ of RAM for production-level Jenkins installation.
- Oracle JDK 11 installed, following our tutorial on installing OpenJDK on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04.
Installing Jenkins on Ubuntu
On Ubuntu, you can install Jenkins from the default repositories through apt but the included version often behind the latest available version.
To take advantage of the most recent stable version of Jenkins features and fixes, use the project-maintained packages to install it as shown.
$ wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add - $ sudo sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list' $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install jenkins
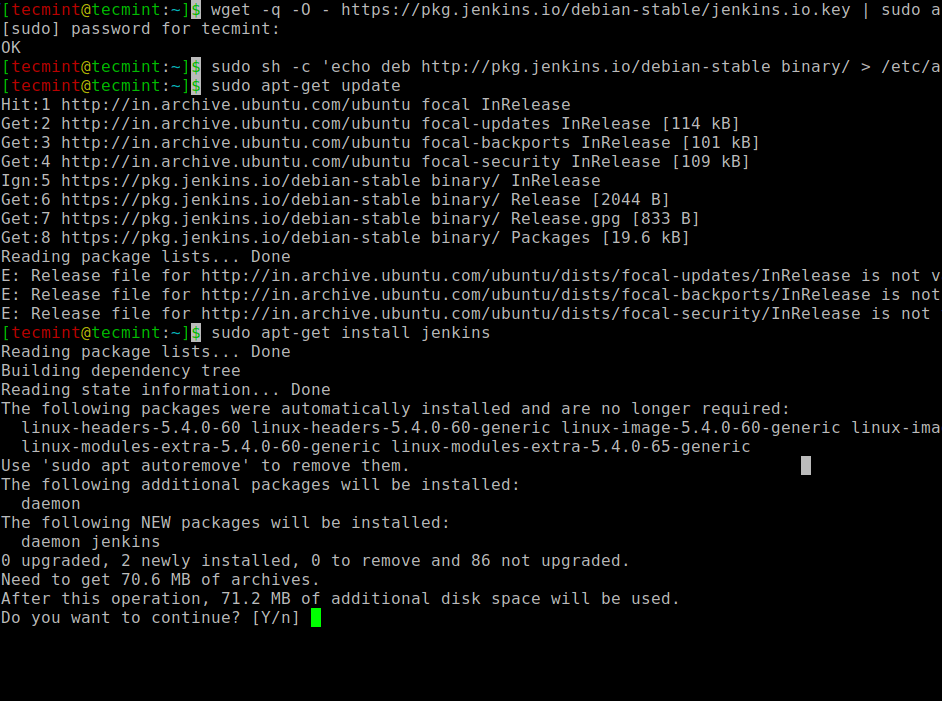
Once Jenkins and its dependencies are installed on the system, you can start, enable, and check the status of the Jenkins server using systemctl commands.
$ sudo systemctl start jenkins $ sudo systemctl enable jenkins $ sudo systemctl status jenkins
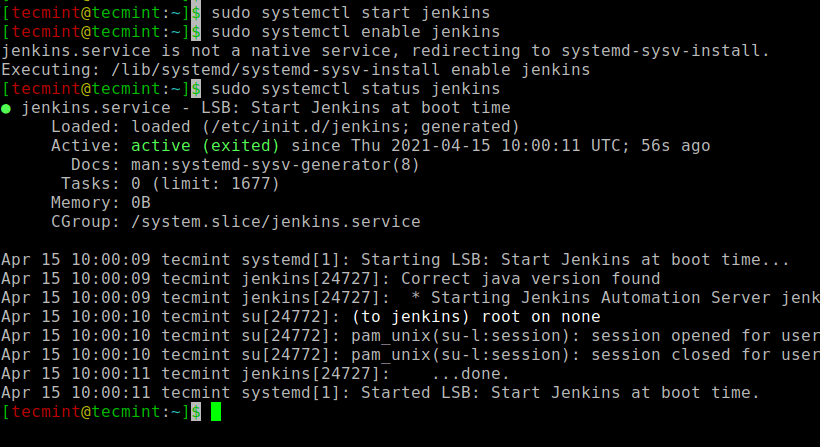
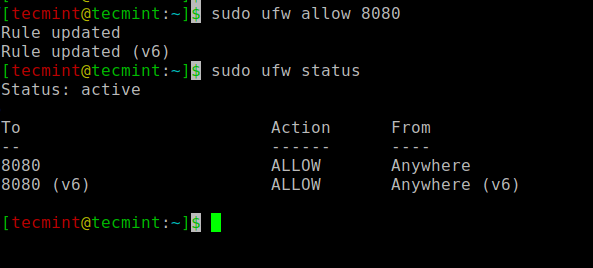
Next, you need to open the default Jenkins port 8080 on ufw firewall as shown.
$ sudo ufw allow 8080 $ sudo ufw status
Now that Jenkins installed and our firewall configured, we can finish the initial setup via the web browser.
Setting Up Jenkins on Ubuntu
To complete Jenkins installation, visit the Jenkins setup page on its default port 8080 at the following address.
http://your_server_ip_or_domain:8080
You should see the Unlock Jenkins screen, that shows the location of the initial password:
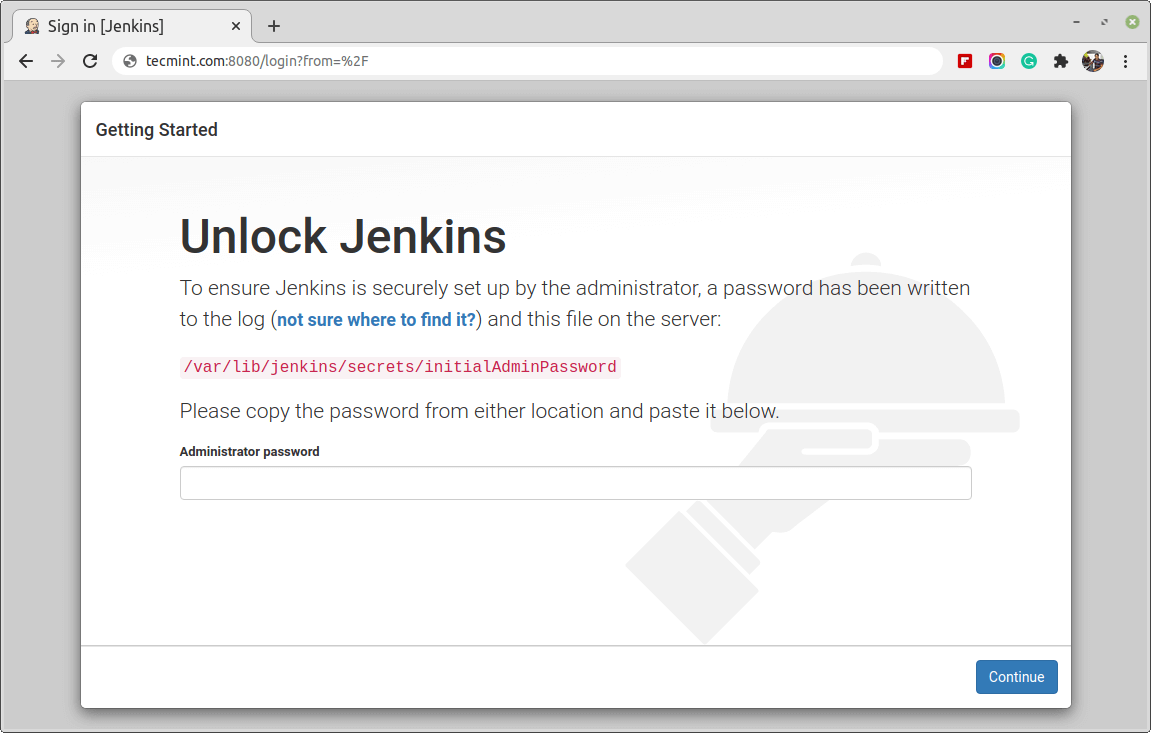
Now run the following cat command to view the password:
$ sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
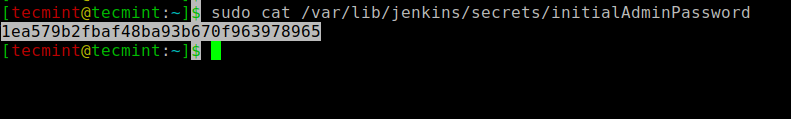
Next, copy this 32-character password and paste it into the Administrator password field, then click Continue.

Next, you will get Customize Jenkins section, here you will get the option of installing suggested plugins or selecting specific plugins. We will choose the Install suggested plugins option, which will immediately start the installation process.
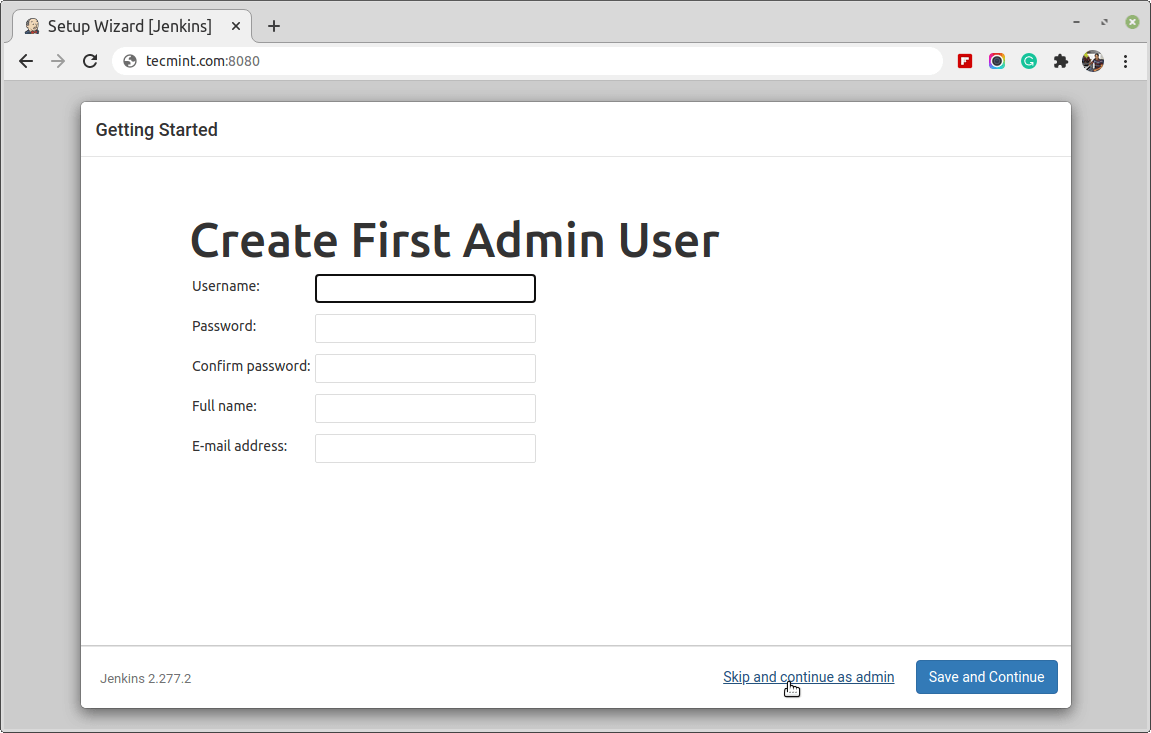
Once the Jenkins installation is finished, you will be asked to create a first administrative user. You can skip this step and continue as admin to use the initial password that we set above.
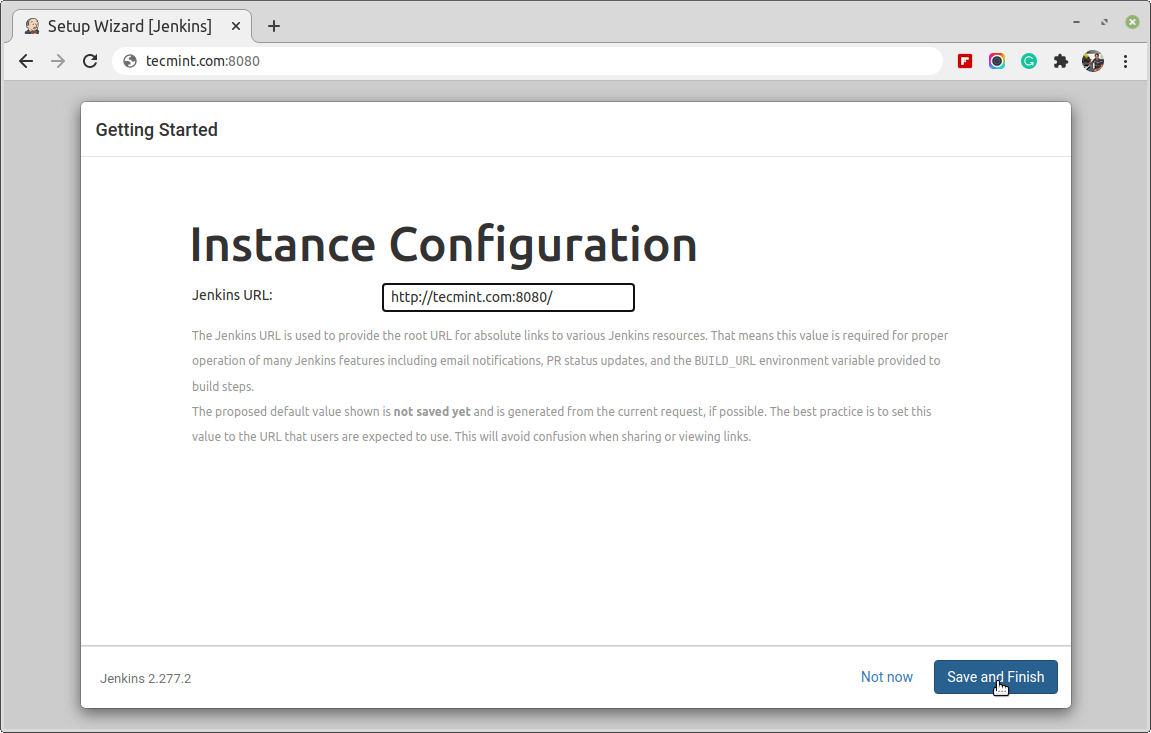
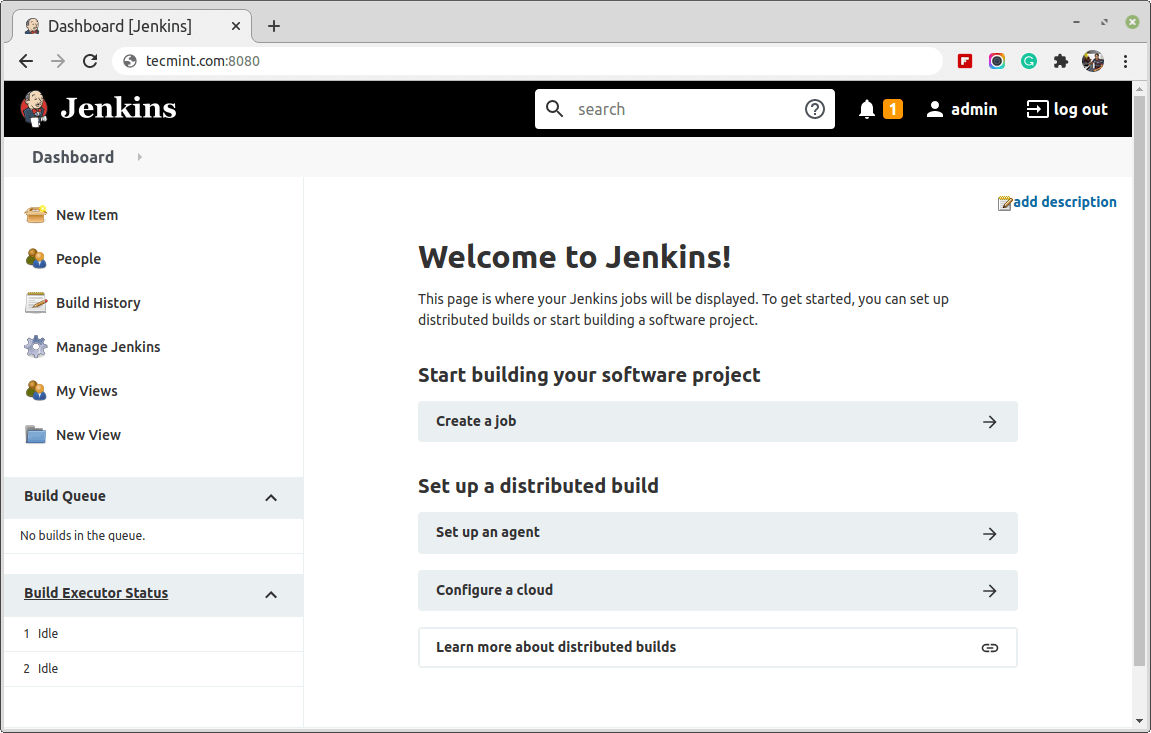
At this point, you have successfully completed the installation of Jenkins.
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to install and set up Jenkins using the project-provided packages on the Ubuntu server. Now you can start exploring Jenkins from the dashboard.
