LibreOffice is an open-source and much powerful personal productivity office suite for Linux, Windows & Mac, that provides feature-rich functions for word documents, data processing, spreadsheets, presentation, drawing, Calc, Math, and much more.
LibreOffice has a large number of satisfied users across the globe with almost 200 million downloads as of now. It supports more than 115 languages and runs on all major operating systems.
The Document Foundation team proudly announced the fresh major release of LibreOffice 7.1.2 on 1, April 2021, is now available for all major platforms including Linux, Windows, and Mac OS.
This new update features a large number of exciting new features, performance, and improvements and is targeted to all kinds of users, but especially appealing for enterprise, early adopters, and power users.
There are many other changes and features included in the newest LibreOffice 7.1.2 – for a complete list of new features, see the release announcement page.
LibreOffice Requirements
- Kernel 3.10 or higher version.
- glibc2 version 2.17 or higher version
- Minimum 256MB and recommended 512MB RAM
- 1.55GB available Hard disk space
- Desktop (Gnome or KDE)
Install LibreOffice on Linux Desktops
The installation instructions provided here are for LibreOffice 7.1.2 using the language US English on a 64-Bit system. For 32-Bit Systems, LibreOffice dropped the support and no longer provide 32-bit binary releases.
Step 1: Downloading LibreOffice
Go to the official LibreOffice download page and grab the latest version that bundled with all the binary packages as a .tar.gz archive file. Alternatively, you can use the following wget command to download the LibreOffice directly in the terminal as shown.
For RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
# cd /tmp # wget http://download.documentfoundation.org/libreoffice/stable/7.1.2/rpm/x86_64/LibreOffice_7.1.2_Linux_x86-64_rpm.tar.gz
For Debian/Ubuntu/LinuxMint
$ sudo cd /tmp $ sudo https://download.documentfoundation.org/libreoffice/stable/7.1.2/deb/x86_64/LibreOffice_7.1.2_Linux_x86-64_deb.tar.gz
Step 2: Removing Old LibreOffice or OpenOffice Versions
If any previously installed LibreOffice or OpenOffice versions you have, remove them using the following command.
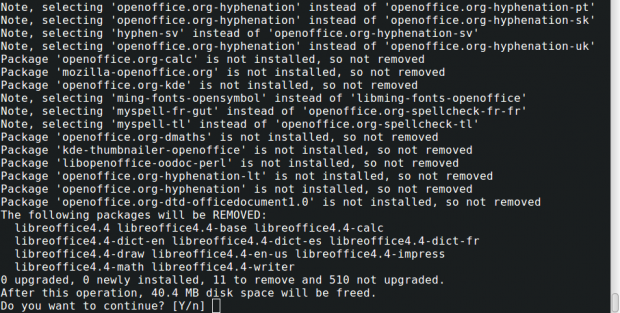
# yum remove openoffice* libreoffice* [on RedHat based Systems]
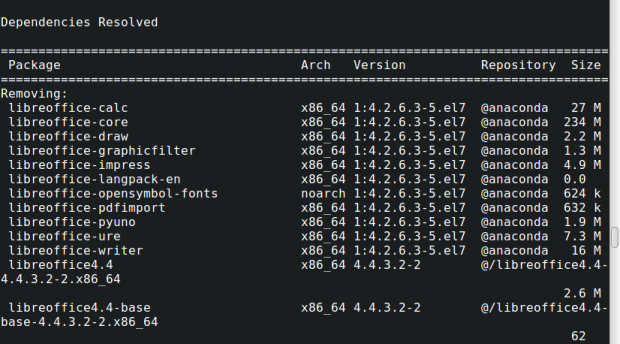
$ sudo apt-get remove openoffice* libreoffice* [On Debian based Systems]
Step 3: Extracting LibreOffice Package
After downloading the LibreOffice package, use the tar command to extract it under /tmp directory or in a directory of your choice.
On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
# tar zxvf LibreOffice_7.1.2_Linux_x86-64_rpm.tar.gz
On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint
$ sudo tar zxvf LibreOffice_7.1.2_Linux_x86-64_deb.tar.gz
Step 4: Installing LibreOffice in Linux Desktop
After extracting the package, you will get a directory and under this, there will be a sub-directory called RPMS or DEBS. Now, run the following command to install it.
On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
# cd /tmp/LibreOffice_7.1.2.2_Linux_x86-64_rpm/RPMS/ # yum localinstall *.rpm OR # dnf install *.rpm [On Fedora 23+ versions]
On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint
$ sudo cd /tmp/LibreOffice_7.1.2.2_Linux_x86-64_deb/DEBS/ $ sudo dpkg -i *.deb
Step 5: Starting LibreOffice in Linux
Once the installation process completes you will have LibreOffice icons in your desktop under Applications –> Office menu or start the application by executing the following command on the terminal.
# libreoffice7.1
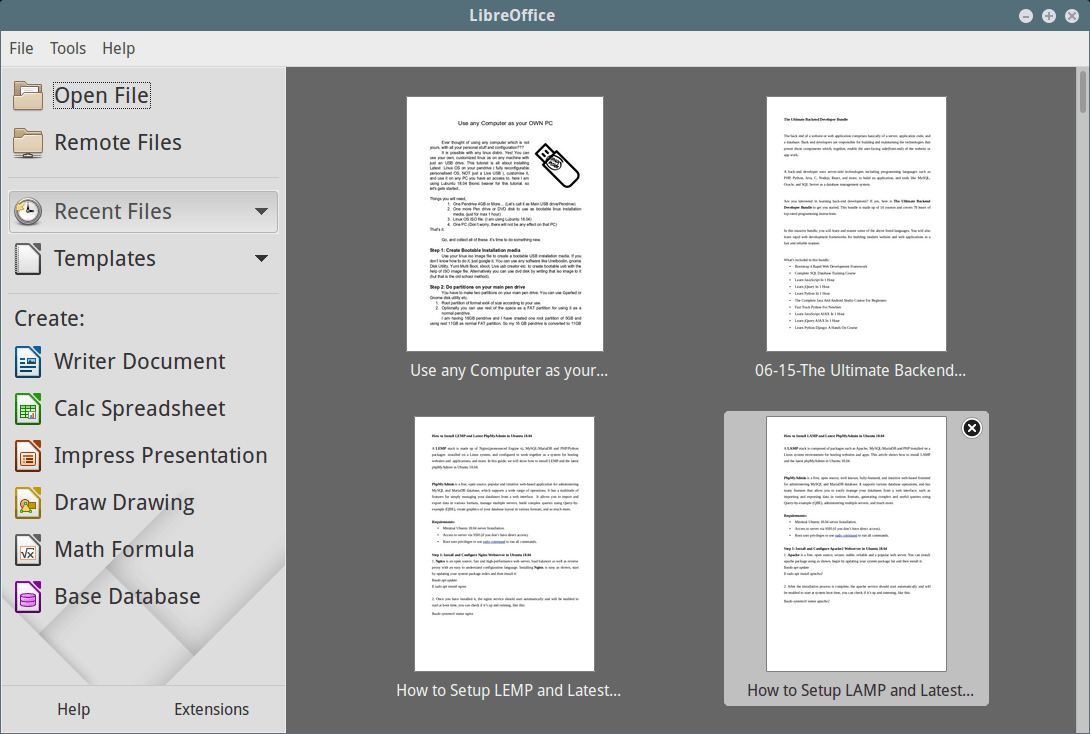
Step 6: Screenshot of LibreOffice 7.1.2
Please see the attached screenshot of the LibreOffice 7.1.2 application under my CentOS 7.0.
Step 7: Installing a Language Pack in LibreOffice
If you would like to install LibreOffice in your preferred language, you should select your language pack for installation. The installation instructions can be found in the Language Pack section.
