MongoDB is an open-source, document database based on the cutting edge technology of NoSQL. It supports the development of modern web applications, with features such as strong consistency, flexibility, expressive query languages, and secondary indexes plus a lot more. Additionally, it offers organizations great scalability and performance for building modern applications with powerful and mission-critical databases.
In this article, you will learn how to install and configure the latest version of MongoDB 4.4 Community Edition on Ubuntu LTS (long-term support) releases of Ubuntu Linux using the apt package manager.
Platform Support
MongoDB 4.4 Community Edition holds the following 64-bit Ubuntu LTS (long-term support) releases:
- 20.04 LTS (“Focal”)
- 18.04 LTS (“Bionic”)
- 16.04 LTS (“Xenial”)
The default Ubuntu repositories offer an outdated MongoDB version, therefore we will install and configure the latest MongoDB from the official MongoDB repository on the Ubuntu server.
Step 1: Adding the MongoDB Repository on Ubuntu
1. To install the latest version of MongoDB Community Edition on your Ubuntu server, you need to install necessary dependencies as shown.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install dirmngr gnupg apt-transport-https ca-certificates software-properties-common
2. Next, import the MongoDB public GPG Key used by the package management system using the following wget command.
$ wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.4.asc | sudo apt-key add -

3. After that, create the list file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.4.list that contains the MongoDB repository details under /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory for your version of Ubuntu.
Now run the following command as per your version of Ubuntu:
Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal)
$ echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu focal/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.4.list
Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic)
$ echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.4.list
Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial)
$ echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu xenial/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.4.list
Then save the file and close it.
4. Next, run the following command to reload the local package database.
$ sudo apt-get update
Step 2: Installing MongoDB Database on Ubuntu
5. Now that MongoDB repository is enabled, you can install the latest stable version by running the following command.
$ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
During the MongoDB installation, it will create the configuration file /etc/mongod.conf, data directory /var/lib/mongodb and the log directory /var/log/mongodb.
By default, MongoDB runs using the mongodb user account. If you change the user, you must also change the permission to the data and log directories to assign access to these directories.
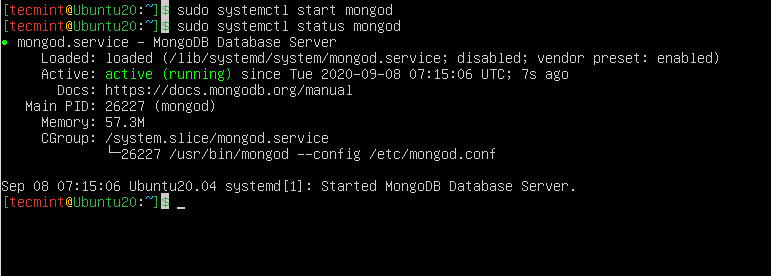
6. Then start and verify the mongod process by running the following command.
------------ systemd (systemctl) ------------ $ sudo systemctl start mongod $ sudo systemctl status mongod ------------ System V Init ------------ $ sudo service mongod start $ sudo service mongod status
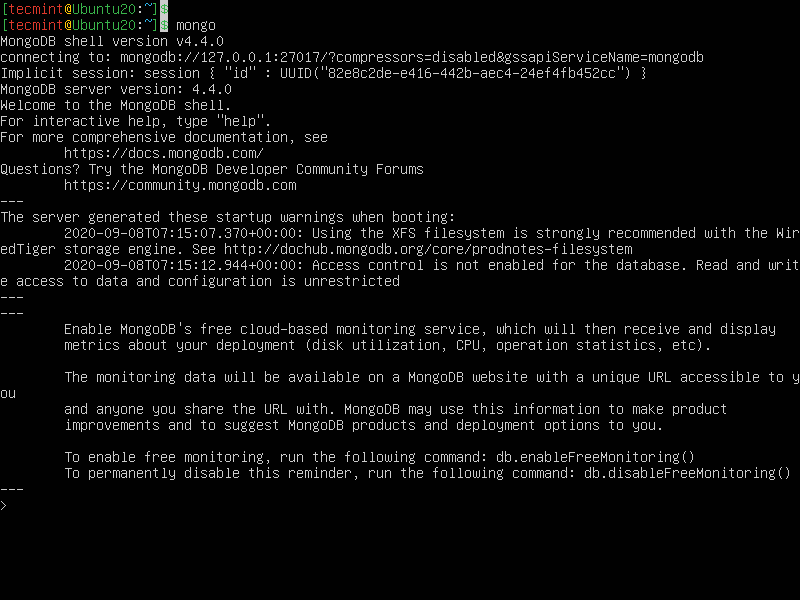
7. Now start a mongo shell without any options to connect to a mongod that is running on your localhost with default port 27017.
$ mongo
Uninstall MongoDB Community Edition
To completely remove MongoDB including MongoDB applications, the configuration files, and any directories containing data and logs, issue the following commands.
$ sudo service mongod stop $ sudo apt-get purge mongodb-org* $ sudo rm -r /var/log/mongodb $ sudo rm -r /var/lib/mongodb
I hope you find this guide useful, for any questions or additional information, you can use the comment section below to air out your concerns.
