Odoo is a full-featured, extensible open-source ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software built using Python and PostgresSQL database for data storage.
It is a suite of open-source business applications, that consists of multiple apps under various categories such as website, sales, finances, operations, manufacturing, human resource (HR), communication, marketing, and customization tools.
The main apps include a website builder, CRM (Content Relationship Manager), a fully-functional eCommerce, marketing app, HR app, accounting tool, inventory app, point of sale app, project management app, and many more.
In this article, we will show you how to install the Odoo 13 Community Edition (CE) on Ubuntu 18.04 or above.
Step 1: Installing PostgreSQL and Wkhtmltopdf on Ubuntu
1. To run Odoo properly, you need a PostgreSQL database server, which can be installed from the default repositories as shown.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install postgresql
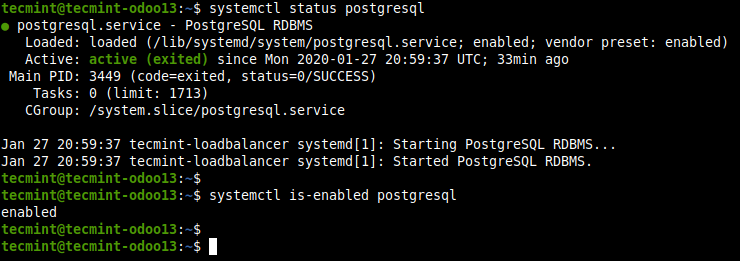
2. Once the PostgresSQL installation is complete you need to check a few things. During the installation process, the installer is configured to start the postgresql service and enable it to automatically start when the server is rebooted. To check if the service is up and running, and is enabled, run the following systemctl commands.
$ systemctl status postgresql $ systemctl is-enabled postgresql
3. Next, you need to install Wkhtmltopdf – is an open-source, small command-line utility that converts an HTML page to PDF document or an image using WebKit.
Odoo 13 requires wkhtmltopdf v0.12.05 which is not provided in the Ubuntu repositories. So you need to install it manually by running the following commands.
$ wget https://github.com/wkhtmltopdf/wkhtmltopdf/releases/download/0.12.5/wkhtmltox_0.12.5-1.bionic_amd64.deb $ sudo dpkg -i wkhtmltox_0.12.5-1.bionic_amd64.deb $ sudo apt -f install
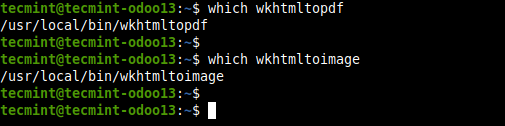
4. Verify that Wkhtmltopdf is successfully installed on your machine.
$ which wkhtmltopdf $ which wkhtmltoimage
Step 2: Installing Odoo 13 in Ubuntu
5. We will be using official Odoo repository to install Odoo Community Edition by executing the following commands.
$ sudo wget -O - https://nightly.odoo.com/odoo.key | sudo apt-key add - $ sudo echo "deb http://nightly.odoo.com/13.0/nightly/deb/ ./" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/odoo.list $ sudo apt-get update && apt-get install odoo
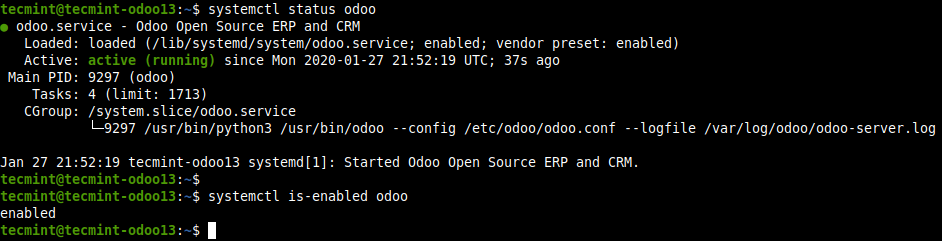
6. Once Odoo installed, you can verify the service is up and running and is enabled to automatically start at system boot.
$ systemctl status odoo $ systemctl is-enabled odoo
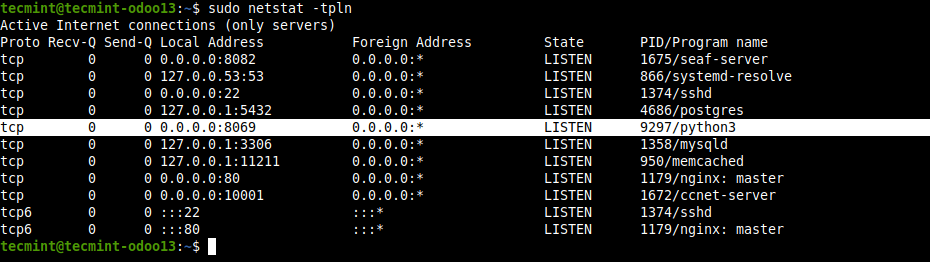
7. By default, Odoo listens on port 8069 and you can verify it using the netstat or ss tools as follows. This is another way to confirm that Odoo is up and running.
$ sudo netstat -tpln OR $ sudo ss -tpln
Step 3: Install and Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy for Odoo
8. To enable users to access the Odoo web interface without typing the port number, you can configure Odoo to be accessed using a sub-domain using an Nginx reverse proxy environment.
To configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy for Odoo, first, you need to install Nginx as shown.
$ sudo apt install nginx
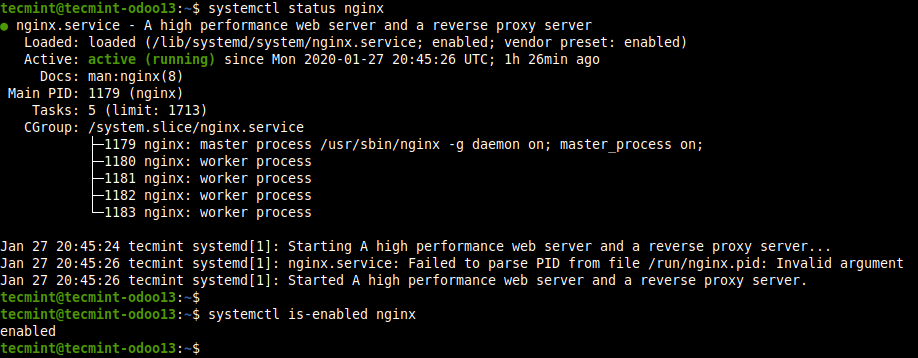
9. When the installation is complete, check if the Nginx service is up and running, is enabled as well.
$ systemctl status nginx $ systemctl is-enabled nginx
10. Next, create an Nginx server block for Odoo in the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/odoo.conf as shown.
$ sudo vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/odoo.conf
Then copy and paste the following configuration in the file. This is a simple configuration sufficient to run your Odoo system, you can add more configurations by reading the Nginx documentation to suit your environment.
server {
listen 80;
server_name odoo.tecmint.lan; access_log /var/log/nginx/odoo_access.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/odoo_error.log; proxy_buffers 16 64k; proxy_buffer_size 128k; location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8069; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; } location ~* /web/static/ { proxy_cache_valid 200 60m; proxy_buffering on; expires 864000; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8069; } gzip on; gzip_min_length 1000; }
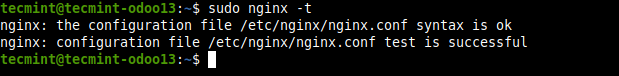
11. After saving the changes in the file. Check the Nginx configuration structure for any syntax errors.
$ sudo nginx -t
12. Now restart the Nginx service to effect the recent changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
13. Importantly, if you have enabled the UFW firewall service enabled and running, you need to allow HTTP and HTTPS requests through the firewall to the Nginx server before starting to access the Odoo web interface.
$ sudo ufw allow http $ sudo ufw allow https $ sudo ufw reload
Step 4: Accessing Odoo Web Administration Interface
14. Next, open a web browser and use the following address to access the Odoo web administration interface.
http://odoo.tecmint.lan
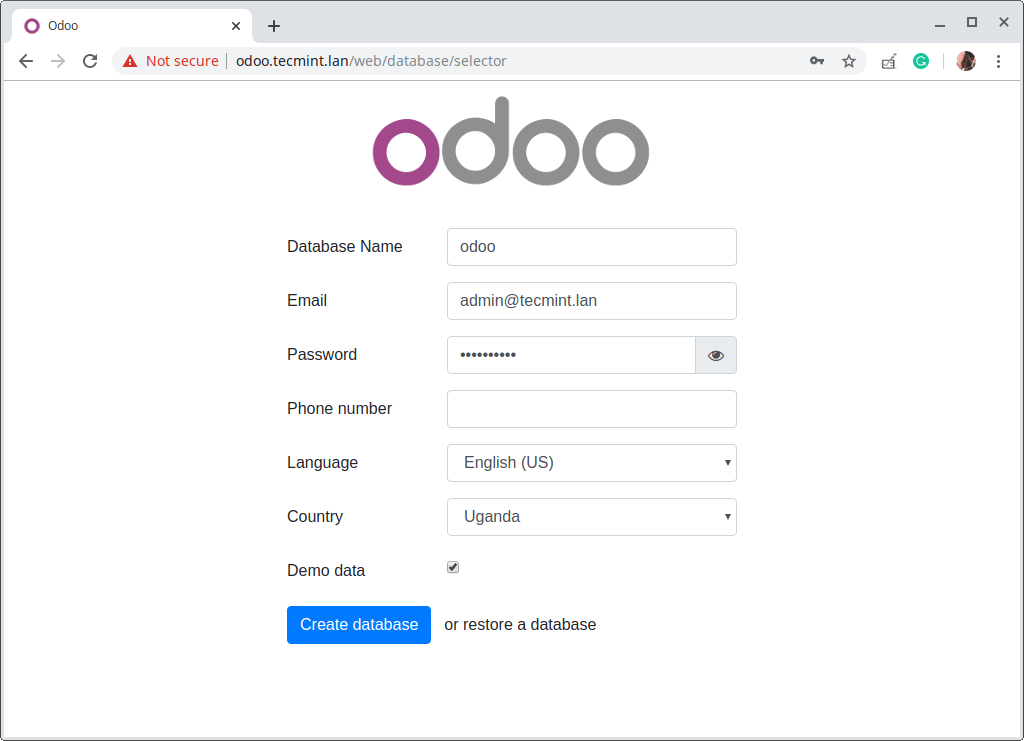
Wait for the interface to load, once it has, you need to create a database for Odoo. Enter a database name, administrator email address, and password. Then select the language and country. You can opt to load sample data or not. Then click Create Database.
15. Then the above page will redirect to the administrator’s dashboard showing the available Odoo apps, as shown in the following screenshot. Click on the Install or Upgrade button on an app to install or upgrade it respectively. To logout, click on Admin dropdown ==> Log out.
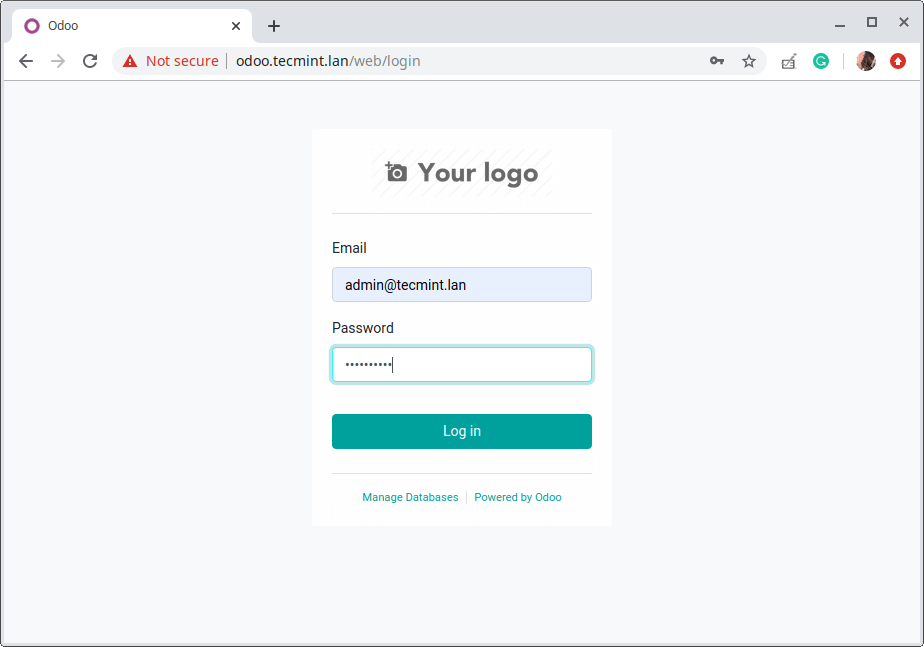
16. The following screenshot shows the Odoo login interface. Use the credentials created in step 14 above to login.
From the screenshot, you can see that the system is not secure as it is running on plain HTTP. So you need to enable HTTPS, especially for a production environment. You can use Let’s Encrypt which is free: How to Secure Nginx with Let’s Encrypt on Ubuntu and Debian.
That’s all for now! You have installed Odoo 13 CE on your Ubuntu server. Although Odoo apps integrate seamlessly out-of-the-box to provide an accomplished, integrated ERP solution, each application can be deployed as a stand-alone application. For more information, see the Odoo 13 documentation.