Netdata is a free and opensource real-time monitoring and troubleshooting tool for cloud servers, containers, applications, and on-premise IT infrastructure. It provides high granular and real-time system metrics such as CPU performance, RAM & disk utilization, and bandwidth statistics, to mention a few.
Additionally, Netdata also provides interactive metric visualizations that can be accessed on a web browser along with intelligent alarms that help in troubleshooting system faults.
Netdata’s cutting edge technology and popularity have earned it a place in Forbes cloud 100 rising stars in 2020, which is no mean feat. In fact, at the time of writing this guide, it has received almost 50,000 Github stars.
There are two ways that you can use to install Netdata. You can right away run an automated script on a BASH shell. This updates your systems and initiates the installation of Netdata, Alternatively, you can clone Netdata’s Git repository and thereafter execute the automated script. The first method is simple and straightforward and it is what we shall focus on in this guide.
In this article, we will see how you can install Netdata on Ubuntu to monitor real-time, performance, and health monitoring of servers and applications.
Supported Platforms
Netdata supports the following Ubuntu LTS distributions:
- Ubuntu 20.04
- Ubuntu 18.04
- Ubuntu 16.04
How to Install Netdata in Ubuntu Linux
To begin the installation, run the command below on your bash terminal to download and execute the script.
$ bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh)
During the execution of the script, the following takes place:
- The script automatically discovers your Linux distribution, updates the package list, and installs all the requisite software packages.
- The latest netdata source tree is downloaded to the /usr/src/netdata.git path.
- The script installs netdata by running the ./netdata-installer.sh script from the source tree.
- An update is made to cron.daily to ensure that netdata is updated on a daily basis.
As the script is run, you will be given tips on how to access Netdata on a browser and how to manage it as a systemd service.
The installation takes a while, so give it about 10 minutes and come back. Finally, you’ll get the output below as the script wraps up the installation.
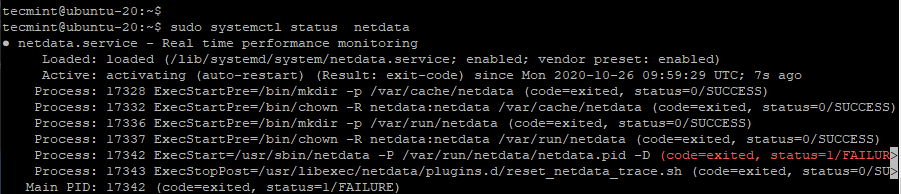
Once installed, start, enable, and verify the status of Netdata as shown.
$ sudo systemctl start netdata $ sudo systemctl enable netdata $ sudo systemctl status netdata
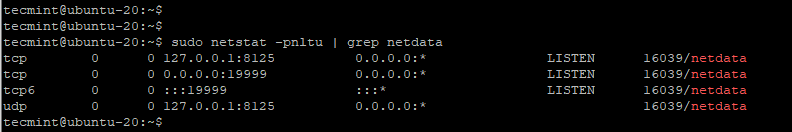
By default, Netdata listens on port 19999 and this can be confirmed using the netstat command as shown.
$ sudo netstat -pnltu | grep netdata
If you have UFW running, make an effort to open port 19999 as this will be required when accessing Netdata on the browser.
$ sudo ufw allow 19999/tcp $ sudo ufw reload
Finally, to access Netdata, switch to your browser and browse the following URL
http://server-ip:19999/
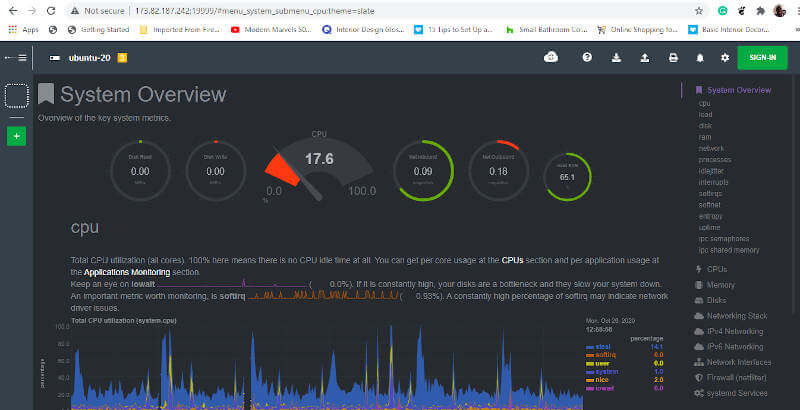
This is what greets you once you browse the URL. In fact, you’ll realize that you won’t be required to login in. All the system’s metrics will be displayed as shown.
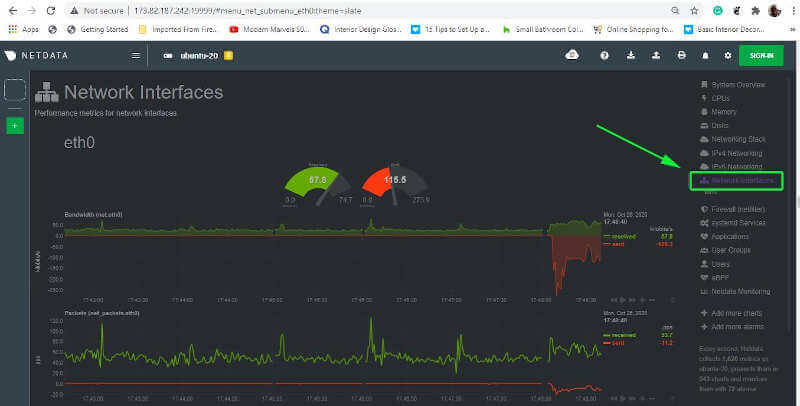
You can flip through various graphs by clicking on your preferred metrics on the right sidebar of the dashboard. For example, to check out the network interface statistics, click on the ‘Network Interfaces‘ option.
This brings us to the end of our topic for today. You’ve just learned how to install the Netdata monitoring tool on Ubuntu. Feel free to check out other graphs on various system metrics.
