In this article, you will learn how to share a wired (Ethernet) internet connection via a wireless hotspot and also how to share a wireless internet connection via a wired connection on a Linux desktop.
This article requires you to have at least two computers: a Linux desktop/laptop with a wireless card and an Ethernet port, then another computer (which may not necessarily be running Linux) with either a wireless card and/or an Ethernet port.
Sharing Wired(Ethernet) Internet Connection Via Wi-Fi Hotspot
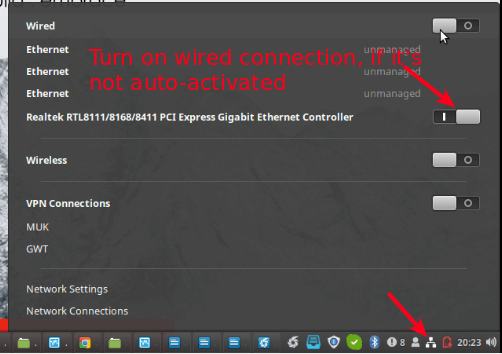
First, connect your computer to a source of internet using an Ethernet cable as shown in the following screenshot.
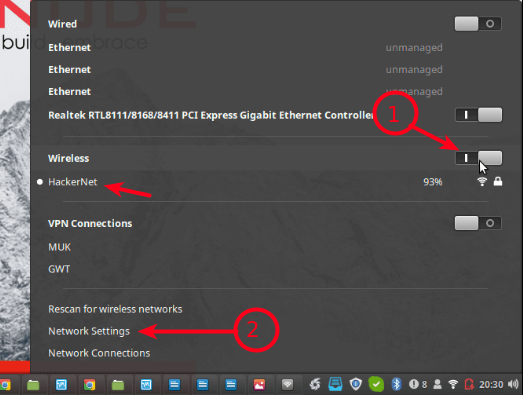
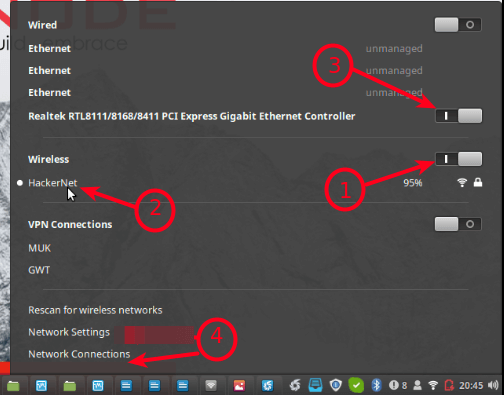
Next, enable Wireless connections, then go to Network Settings as highlighted in the following screenshot.
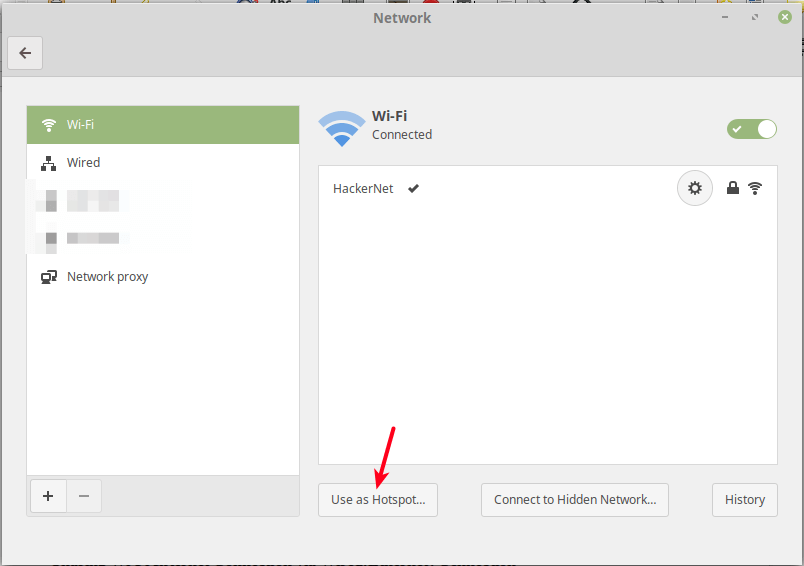
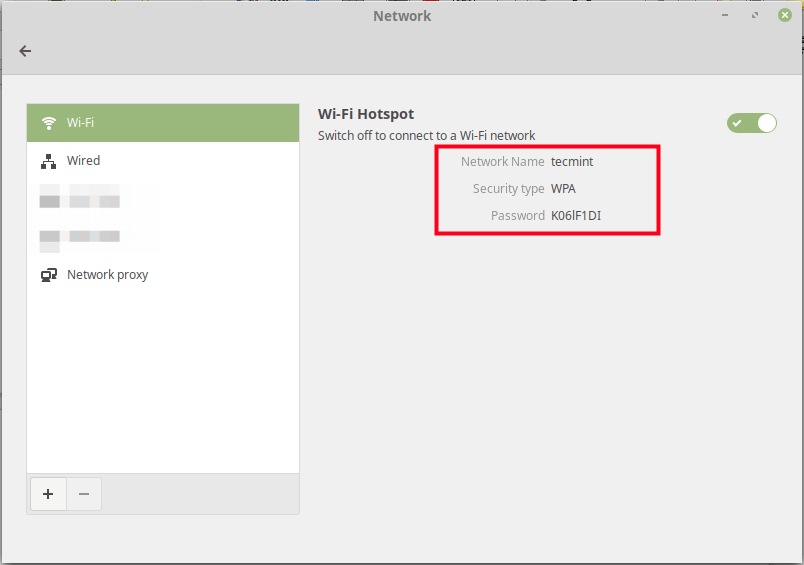
Then click Use as Hotspot as shown in the following screenshot.
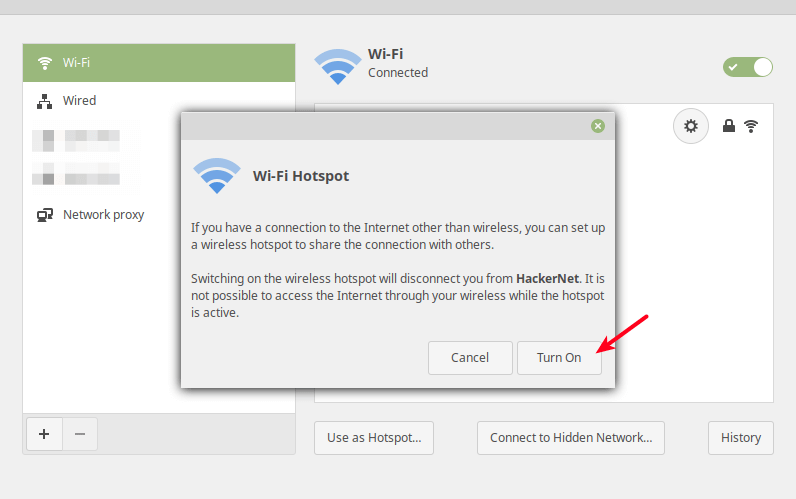
Next, from the pop-up window, click Turn On to activate the wireless hotspot.
Now a wireless hotspot should be created with a name defaulting to the hostname e.g tecmint.
Now you can connect another computer or device via the hot-spot to the internet.
Sharing Wi-Fi Internet Connection via Wired(Ethernet) Connection
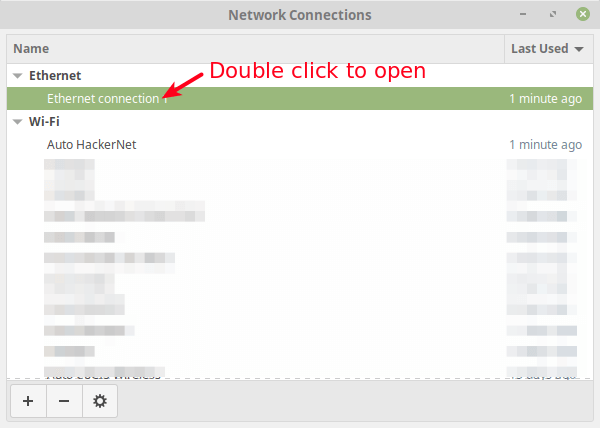
Start by connecting your computer to a wireless connection with access to the internet e.g HackerNet in the test environment. Then connect an Ethernet cable to it and go to Network Connections.
From the pop-up window, select the Wired/Ethernet connection, then go to its settings as described in the following screenshot.
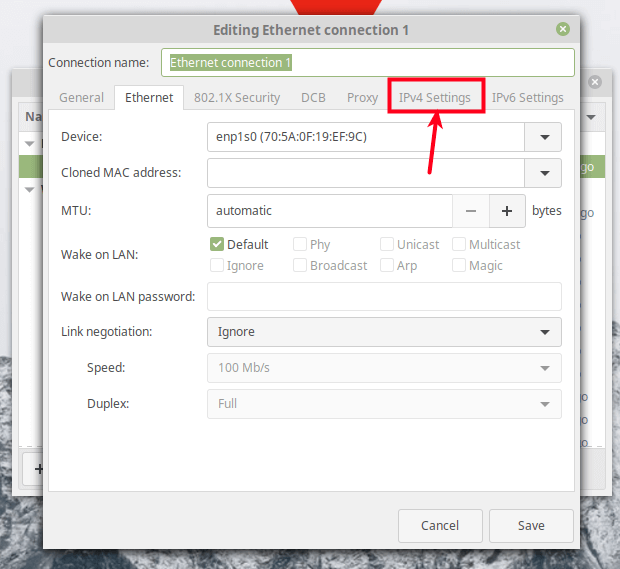
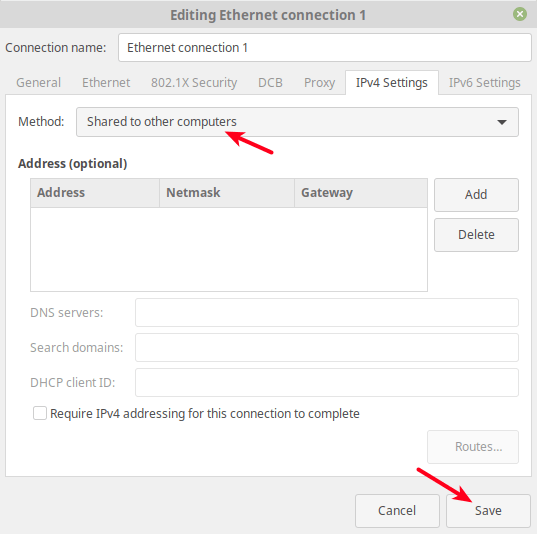
Under the connection settings, go to IPv4 Settings.
Under the IPv4 settings, set the Method to Shared to other computers as shown in the following screenshot. Optionally, you can add the IP address to define the network to use. Then click Save.
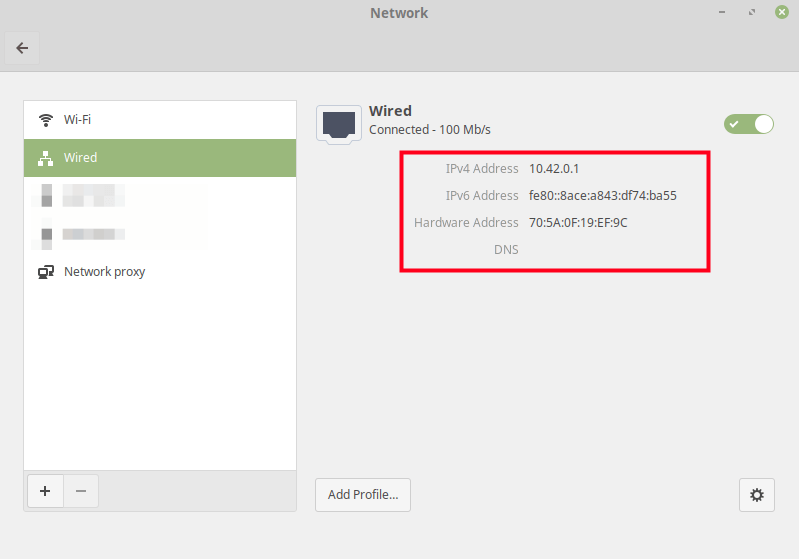
Next, turn the wired connection off then on, to activate it once more. Then open it under Network Connections, it should now be configured for sharing (by having a default IP address of 10.42.0.1) as shown in this screenshot.
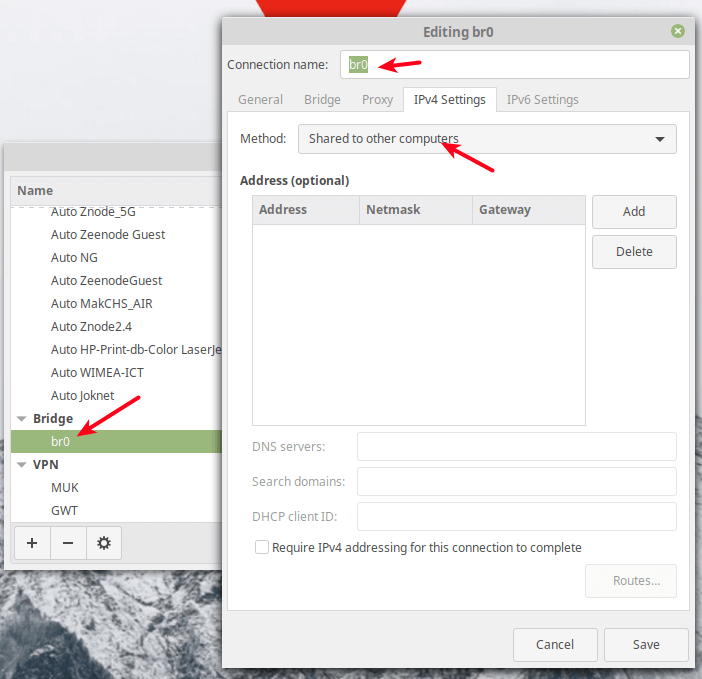
Note: You can also share a bridged interface the same way as the wired interface as shown in the following screenshot.
Go ahead and connect another computer to the other end of the Ethernet cable or an access point to serve many computers/devices. For any inquiries, reach us via the feedback form below.