The primary Application we require to perform our internet activity is a browser, a web browser to be more perfect. Over the Internet, most of our’s activity is logged to the Server/Client machine which includes IP address, Geographical Location, search/activity trends and a whole lot of information which can potentially be very harmful if used intentionally the other way.
Moreover, the National Security Agency (NSA) aka International Spying Agency keeps track of our digital footprints. Not to mention a restricted proxy server which again can be used as a data ripping server is not the answer. And most of the corporates and companies won’t allow you to access a proxy server.
Recommended Read: Top 15 Best Security-Centric Linux Distributions of 2019
So, what we need here is an application, preferably small in size and let it be standalone, portable and which servers the purpose. Here comes an application – the Tor Browser, which has all the above-discussed features and even beyond that.
In this article, we will be discussing the Tor browser, its features, its usages and Area of Application, Installation and other important aspects of The Tor Browser Application.
What is Tor Browser?
Tor is a Freely distributed Application Software, released under BSD style Licensing which allows to surf Internet anonymously, through its safe and reliable onion-like structure.
Tor previously was called ‘The Onion Router‘ because of its structure and functioning mechanism. This application is written in C programming Language.
Features of Tor Browser
- Cross-Platform Availability. i.e., this application is available for Linux, Windows as well as Mac.
- Complex Data encryption before it sent over the Internet.
- Automatic data decryption at client side.
- It is a combination of Firefox Browser + Tor Project.
- It provides anonymity to servers and websites.
- It makes it possible to visit locked websites.
- Performs task without revealing the IP of Source.
- Capable of routing data to/from hidden services and applications behind the firewall.
- Portable – Run a pre-configured web browser directly from the USB storage device. No need to install it locally.
- Available for architectures x86 and x86_64.
- Easy to set FTP with Tor using configuration as “socks4a” proxy on “localhost” port “9050”
- Tor is capable of handling thousands of relay and millions of users.
How Tor Browser Works?
Tor works on the concept of Onion routing. Onion routing resembles an onion in structure. In onion routing, the layers are nested one over the other similar to the layers of an onion.
This nested layer is responsible for encrypting data several times and sends it through virtual circuits. On the client-side, each layer decrypts the data before passing it to the next level. The last layer decrypts the innermost layer of encrypted data before passing the original data to the destination.
In this process of decryption, all the layers function so intelligently that there is no need to reveal IP and Geographical location of User thus limiting any chance of anybody watching your internet connection or the sites you are visiting.
All these working seems a bit complex, but the end-user execution and working of the Tor browser is nothing to worry about. In-fact Tor browser resembles any other browser (Especially Mozilla Firefox) in functioning.
How to Install Tor Browser in Linux
As discussed above, the Tor browser is available for Linux, Windows, and Mac. The user needs to download the latest version (i.e. Tor Browser 9.0.4) application from the link below as per their system and architecture.
After downloading the Tor browser, we need to install it. But the good thing with ‘Tor’ is that we don’t need to install it. It can run directly from a Pen Drive and the browser can be pre-configured. That means plug and Run Feature in a perfect sense of Portability.
After downloading the Tar-ball (*.tar.xz) we need to Extract it.
On 32-Bit System
$ wget https://www.torproject.org/dist/torbrowser/9.0.4/tor-browser-linux32-9.0.4_en-US.tar.xz $ tar xpvf tor-browser-linux32-9.0.4_en-US.tar.xz
On 64-Bit System
$ wget https://www.torproject.org/dist/torbrowser/9.0.4/tor-browser-linux64-9.0.4_en-US.tar.xz $ tar -xpvf tor-browser-linux64-9.0.4_en-US.tar.xz
Note: In the above command we used ‘$‘ which means that the package is extracted as a user and not the root. It is strictly suggested to extract and run the tor browser, not as root.
After successful extraction, we can move the extracted browser anywhere in the system or to any SB Mass Storage device and run the application from the extracted folder as a normal user as shown.
$ cd tor-browser_en-US $ ./start-tor-browser.desktop
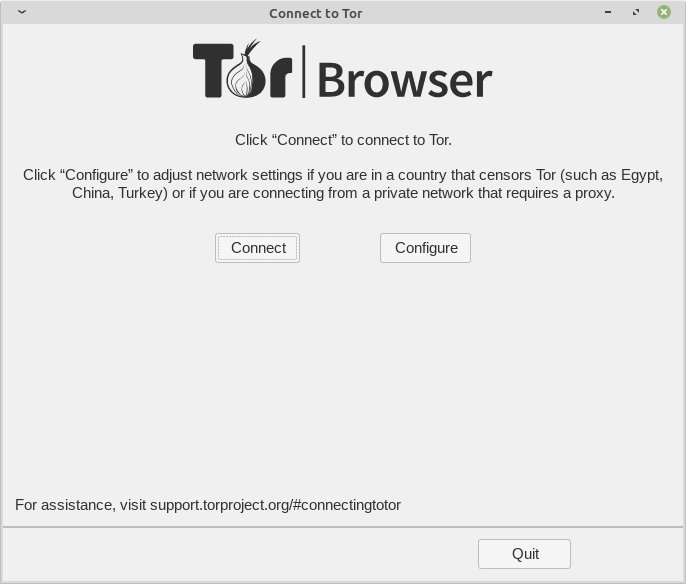
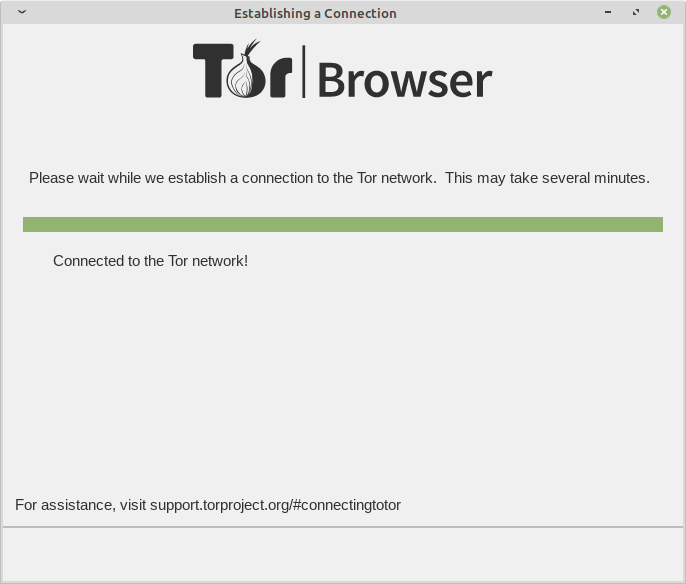
Trying to connect to the Tor Network. Click “Connect” and Tor will do the rest of the settings for you.
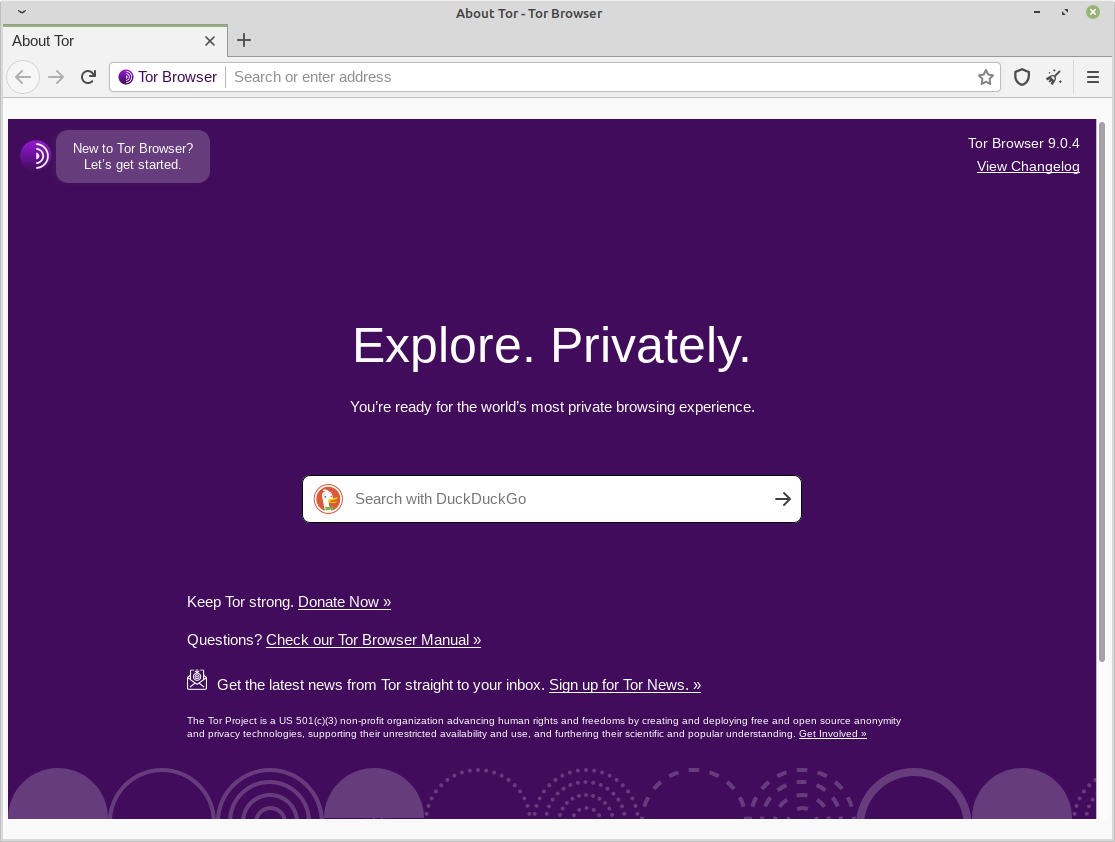
The welcome Window/Tab.
Creating a Tor Desktop Shortcut in Linux
Remember that you need to point to the Tor startup script using text session, every time you want to run Tor. Moreover, a terminal will be busy all the time until you are running tor. How to overcome this and create a desktop/dock-bar Icon?
We need to create tor.desktop the file inside the directory where extracted files reside.
$ touch tor.desktop
Now edit the file using your favorite editor with the text below. Save and exit. I used nano.
$ nano tor.desktop
#!/usr/bin/env xdg-open [Desktop Entry] Encoding=UTF-8 Name=Tor Comment=Anonymous Browse Type=Application Terminal=false Exec=/home/tecmint/Downloads/tor-browser_en-US/start-tor-browser.desktop Icon=/home/tecmint/tor-browser_en-US/Browser/browser/chrome/icons/default/default128.png StartupNotify=true Categories=Network;WebBrowser;
Note: Make sure to replace the path with the location of your tor browser in the above.
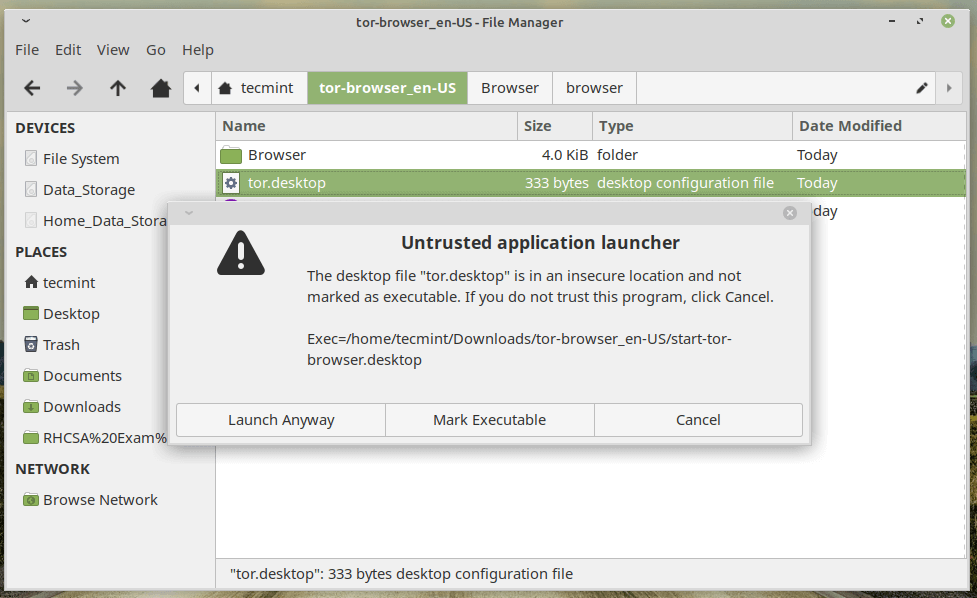
Once done! Double click the file tor.desktop to fire the Tor browser.
Once you trust you might note that the icon of tor.desktop changed.
You may now copy the tor.desktop icon to create a shortcut on Desktop and launch it.
If you are using an older version of Tor, you may update it from the About window.
Usability/Area of Application
- Anonymous communication over the web.
- Surf to Blocked Web Pages.
- Link other Application Viz (FTP) to this secure Internet Browsing Application.
Controversies of Tor-browser
- No security at the boundary of Tor Application i.e., Data Entry and Exit Points.
- A study in 2011 reveals that a specific way of attacking Tor will reveal the IP address of BitTorrent Users.
- Some protocols show the tendency of leaking IP address, revealed in a study.
- An earlier version of Tor bundled with older versions of the Firefox browser was found to be JavaScript Attack Vulnerable.
- Tor Browser Seems to Work slow.
Future of Tor Browser
The Tor browser is promising. Perhaps the first application of its kind is implemented very brilliantly. Tor browser must invest for Support, Scalability, and research for securing the data from the latest attacks. This application is the need for the future.
Conclusion
Tor browser is a must tool in the present time where the organization you are working for doesn’t allow you to access certain websites or if you don’t want others to look into your private business or you don’t want to provide your digital footprints to NSA.
Note: Tor Browser doesn’t provide any safety from Viruses, Trojans or other threats of this kind. Moreover, by writing an article about this we never mean to indulge in illegal activity by hiding our identity over the Internet.
This post is totally for educational purposes and for any illegal use of it neither the author of the post nor Tecmint will be responsible. It is the sole responsibility of the user.
Tor-browser is a wonderful application and you must give it a try. That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting article you people will love to read. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your value-able feedback in our comment section below.