Having written a few top things in the past for Ubuntu systems, it’s that time of the year again for us to revisit the subject of some of the ideal things you need to do in order to successfully configure your Ubuntu operating system for optimal use.
For the uninitiated, Ubuntu is a family of operating systems that are oriented towards newcomers in the Linux world. With the main Ubuntu system using Gnome as the default desktop environment, we have other flavors that use desktops like XFCE, MATE, LXDE, and KDE by default.
[ You might also like: 13 Open Source Linux Desktop Environments ]
So irrespective of the Ubuntu-based system you may have, this guide will work just right for you as well.
1. Update Ubuntu System
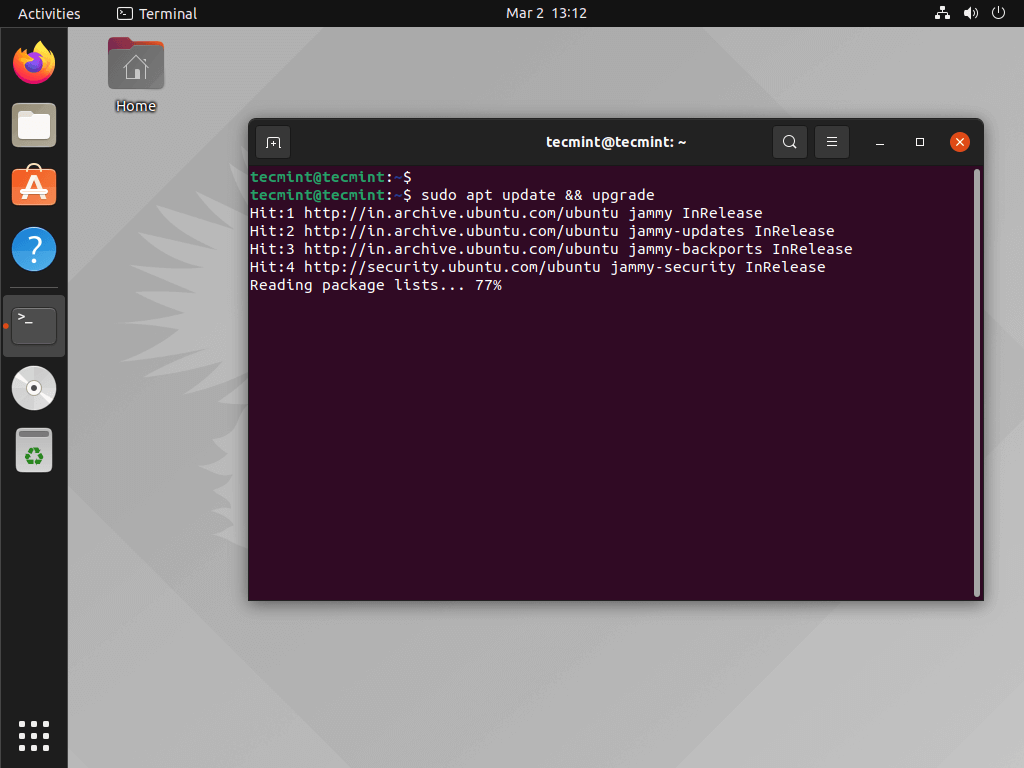
For starters, we will be updating and upgrading our entire system to get it ready for further customizations. Do this by running the command below.
4 sudo apt update && upgrade
2. Update Ubuntu Privacy Settings
If you’re a Linux diehard – you don’t really have to be – then you probably have some privacy concerns that essentially made you abandon Windows for Linux and of course, this is a completely warranted move against the unscrupulous Windows data collection practices. On that note, you should be aware that there’s a certain level of data collection practices built into your Ubuntu system.
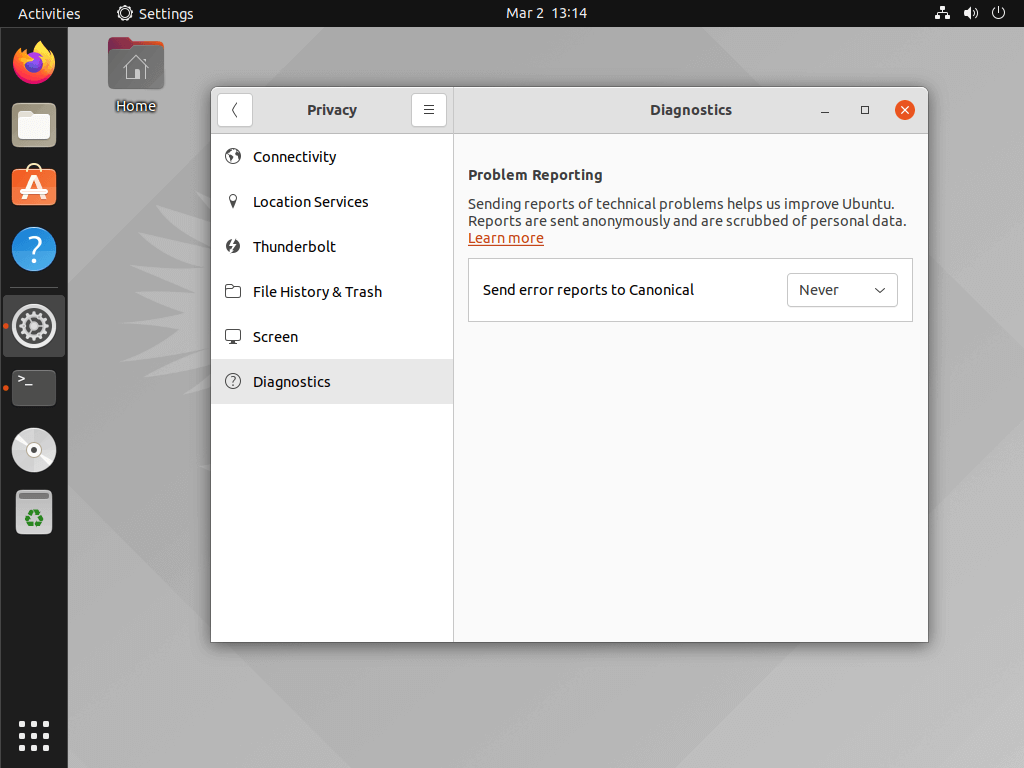
The best practice would be to go to your system setting -> privacy and observe what’s being collected and adjust accordingly. In my specific case, I decided to disable error reports to Canonical under diagnostics, turned off location services and usage history as well. These options happen to be the main concerns for me.. you might be inclined to turn off other options but let that be at your discretion.
3. Install Gnome Tweak in Ubuntu
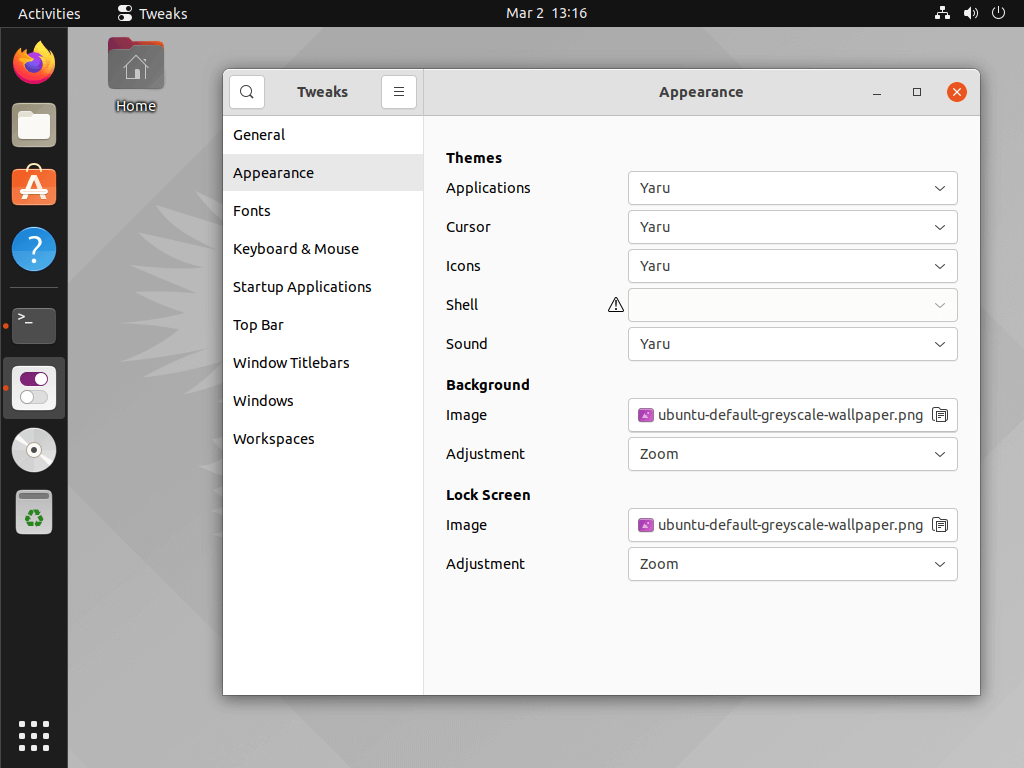
With Gnome as the default desktop environment on our test system, it is a no-brainer; and even better, it doesn’t need Gnome DE as it works just well with any other flavor of Ubuntu you might want to install. Gnome Tweak Tool is a powerful swiss army knife that works across the board irrespective of the desktop environment.
It’s packed full of features ranging from appearance configuration – including themes, top bar options, font change, startup apps, windows, and workspaces.
Gnome Tweak tool is available in the default Ubuntu repository and can be installed using the command below.
$ sudo apt install gnome-tweaks
4. Install Ubuntu Restricted Extras
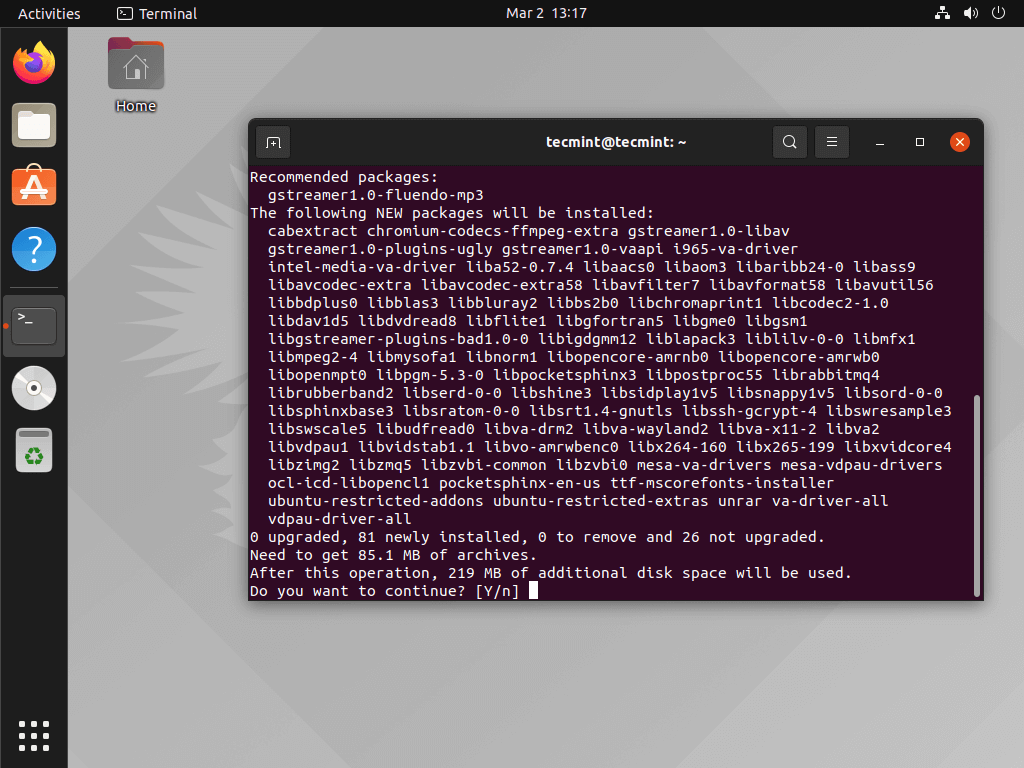
As an option equally available in the Ubuntu repo, you can configure your installation with Ubuntu restricted extras that will essentially configure the codecs necessary to play media files that your default Gnome video player, Totem, will not be able to set up.
$ sudo apt install ubuntu-restricted-extras
This will essentially enable you to play most videos and audio via your Ubuntu default players.
5. Install a List of Important Applications
Ubuntu, for the most part, is barebones without a lot of third-party applications available with your default install. Use your Ubuntu software center to download the applications listed below or go the alternative route of using the terminal (which is my preferred way). With the exception of Google Chrome, the Ubuntu software center is great for the rest of the apps you need but rather slow for a quick install.
Google Chrome
Head over to the official Google Chrome website to download the Google Chrome .deb package for your Ubuntu system. If you’d like something different, consider Chromium although the experience is not necessarily up to par anymore as Google Chrome is still superior to Chromium.
Use the command below to download Chromium onto your Ubuntu system.
$ sudo apt install chromium
Synaptic
The synaptic package manager is a graphical user interface for the apt package manager for an easier configuration of your debian applications.
$ sudo apt install synaptic
VLC Media Player
A commonly underrated media player, VLC, is next to perfect for just about any system and I don’t see any reason why it’s been bundled by default considering the incredible set of functionalities that come with the system.
$ sudo apt install vlc
Gimp
If you’re keen on the adobe ecosystem, then you know why Gimp is important for those that are artistic at heart – or even if you’re just a daring user. Gimp is the ultimate representation of what’s possible when it comes to graphics work/image manipulation on Linux-based systems.
$ sudo apt install gimp
Shutter
Shutter for Linux is my favorite screenshot tool that enables the power of screen capture at your fingertips. It is quite extensive as it prides itself in a well-rounded feature-set that doesn’t do too much or too little.
It’s just the perfect nifty tool with editing in tow that you just can’t go wrong with. Install Shutter using the command below
$ sudo apt install shutter
Thunderbird
Are you a heavy email user? Of course, I’m talking about myself and pretty much anyone with an email address for school, work, or personal. As a result, you’re probably familiar with the fact that It can quickly become cumbersome to manage multiple accounts within your browser.
And this is where Thunderbird comes in with native features that drive your productivity to the max while remaining as native as possible in your system with notifications and multi-accounts support in tow.
With a pretty painless and wizard-oriented setup, you will be up and running in no time with your emails. Download onto your Ubuntu system using the command below.
$ sudo apt install thunderbird
Timeshift
If you’re familiar with the Mac’s Time Machine then you know very well that it is a pretty ingenious way to ensure the safe recovery of your operating system if anything were to break and that’s exactly what Timeshift is for Linux-based systems.
In order to get it set up on your laptop or desktop, use the command below to add the ppa before running the install command.
$ sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa $ sudo apt install timeshift $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install timeshift
Once you’re done with the installation, you can open the application to configure your first backup.
6. Install Graphics Driver in Ubuntu
You want to install the proper graphics driver of your Ubuntu system to enable smooth rendering of the GUI; this would mostly be required too if you’re looking to game with your PC via Steam, Video editing, and so on.
Type in “software and updates” in the dash and go to the “additional drivers tab”; select as needed and apply changes.
7. Extras + Aesthetics
-
- Move the panel from the left to the bottom of your screen.
- Install Gdebi for a much easier and less bloated front-end package install –
sudo apt install gdebi. - Install Glimpse an alternative to GIMP, based on GIMP –
sudo apt install glimpse. - Switch to dark mode – easier on the eyes. Under settings,> appearance, Select ‘Dark Windows’ and voila, you have a much less infuriating GUI.
- Enhance productivity with minimize on click using the following command in your terminal:
$ gsettings set org.gnome.shell.extensions.dash-to-dock click-action 'minimize'
- Install Gnome Shell extensions using
$ sudo apt install gnome-shell-extensionsafter which you can proceed to extensions under Gnome Tweak, disable Ubuntu dock and desktop icons.
We recommend that you go through with the list and you’ll just be ready to enjoy the rest of the Ubuntu experience as long as you need to.
From this point, you can now tailor the system to some other specific needs you might have; thereafter, it’s silky smooth sailing with this LTS release. If you do encounter any problems installing, or configuring the system as guided above, kindly let us know in the comments below.
