Linux is by default a multi-user system (meaning many users can connect to it simultaneously and work), thus user management is one of the fundamental tasks of a system administrator. User management includes everything from creating, updating, and deleting user accounts or user groups on a Linux system.
In this short quick article, you will learn how to add or remove a user from a group in a Linux system.
Check a User Group in Linux
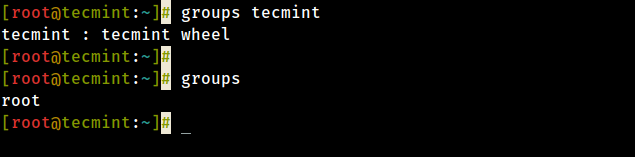
To check a user group, just run the following groups command and provide the username (tecmint in this example) as an argument.
# groups tecmint tecmint : tecmint wheel
To check your own groups, just run the groups command without any argument.
# group root
Add a User to a Group in Linux
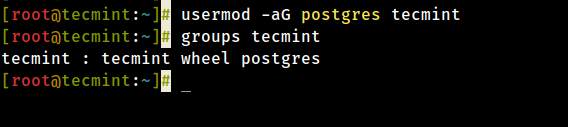
Before trying to add a user to a group, ensure that the user exists on the system. To add a user to a certain group, use the usermod command with the -a flag which tells the usermod to add a user to the supplementary group(s), and the -G option specifies the actual groups in the following format.
In this example, tecmint is the username and postgres is the group name:
# usermod -aG postgres tecmint # groups tecmint
Remove a User from a Group in Linux
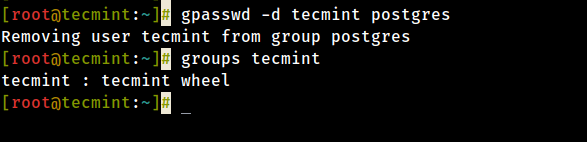
To remove a user from a group, use the gpasswd command with the -d option as follows.
# gpasswd -d tecmint postgres # groups tecmint
Additionally, on Ubuntu and it’s derivative, you can remove a user from a specific group using the deluser command as follows (where tecmint is the username and postgres is the group name).
$ sudo deluser tecmint postgres
For more information, see the man pages for each of the different commands we have used in this article.
You will also find the following user management guides very useful:
- 3 Ways to Change a Users Default Shell in Linux
- How to Monitor Linux Commands Executed by System Users in Real-time
- whowatch – Monitor Linux Users and Processes in Real-Time
- How to Create Multiple User Accounts in Linux
- How to Force User to Change Password at Next Login in Linux
- How to Manage User Password Expiration and Aging in Linux
- How to Lock User Accounts After Failed Login Attempts
