While working with configuration files in Linux, sometimes you need to append text such as configuration parameters to an existing file. To append simply means to add text to the end or bottom of a file.
In this short article, you will learn different ways to append text to the end of a file in Linux.
Append Text Using >> Operator
The >> operator redirects output to a file, if the file doesn’t exist, it is created but if it exists, the output will be appended at the end of the file.
For example, you can use the echo command to append the text to the end of the file as shown.
# echo "/mnt/pg_master/wal_archives 10.20.20.5(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" >> /etc/exports
Alternatively, you can use the printf command (do not forget to use \n character to add the next line).
# printf "/mnt/pg_master/wal_archives 10.20.20.5(rw,sync,no_root_squash)\n" >> /etc/exports
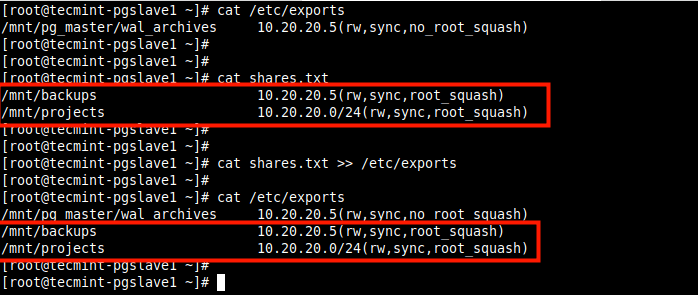
You can also use the cat command to concatenate text from one or more files and append it to another file.
In the following example, the additional file system shares to be appended in the /etc/exports configuration file are added in a text file called shares.txt.
# cat /etc/exports # cat shares.txt # cat shares.txt >> /etc/exports # cat /etc/exports
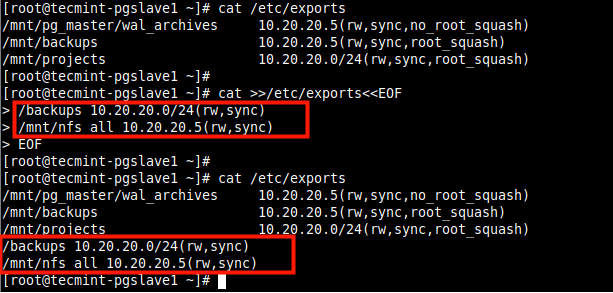
Besides, you can also use the following here document to append the configuration text to the end of the file as shown.
# cat /etc/exports # cat >>/etc/exports<s<EOF > /backups 10.20.20.0/24(rw,sync) > /mnt/nfs_all 10.20.20.5(rw,sync) > EOF # cat /etc/exports
Attention: Do not mistake the > redirection operator for >>; using > with an existing file will delete the contents of that file and then overwrites it. This may result in data loss.
Append Text Using tee Command
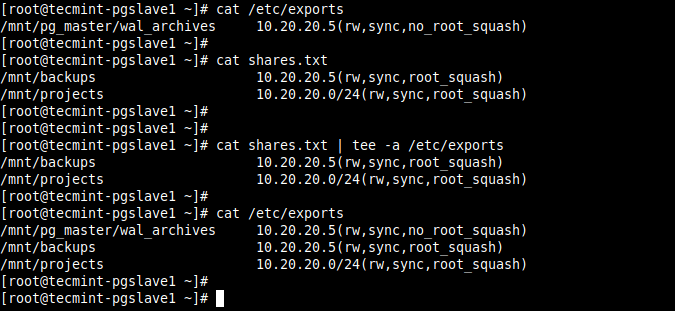
The tee command copies text from standard input and pastes/writes it to standard output and files. You can use its -a flag to append text to the end of a file as shown.
# echo "/mnt/pg_master/wal_archives 10.20.20.5(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" | tee -a /etc/exports OR # cat shares.txt | tee -a /etc/exports
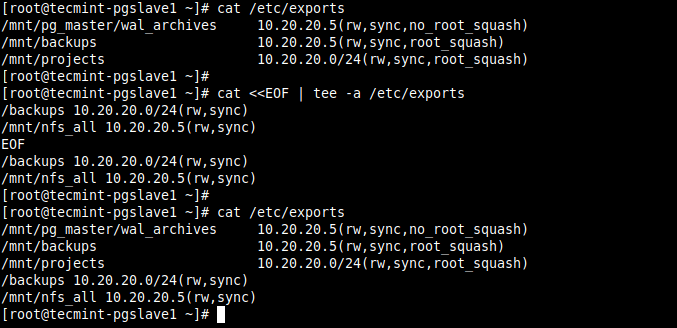
You can also use a here document with the tee command.
# cat <<EOF | tee -a /etc/exports >/backups 10.20.20.0/24(rw,sync) >/mnt/nfs_all 10.20.20.5(rw,sync) EOF
You might also like to read these related articles.
- How to Run Commands from Standard Input Using Tee and Xargs in Linux
- Learn The Basics of How Linux I/O (Input/Output) Redirection Works
- How to Save Command Output to a File in Linux
- How to Count Word Occurrences in a Text File
That’s it! You have learned how to append text to the end of a file in Linux. If you have questions or thoughts to share, reach us via the feedback form below.