As a Linux administrator, you must periodically check which files and folders are consuming more disk space. It is very necessary to find unnecessary junk and free up them from your hard disk.
This brief tutorial describes how to find the largest files and folders in the Linux file system using du (disk usage) and find command. If you want to learn more about these two commands, then head over to the following articles.
- Learn 10 Useful ‘du’ (Disk Usage) Commands in Linux
- Master the ‘Find’ Command with these 35 Practical Examples
How to Find Biggest Files and Directories in Linux
Run the following command to find out top biggest directories under /home partition.
# du -a /home | sort -n -r | head -n 5

The above command displays the biggest 5 directories of my /home partition.
Find Largest Directories in Linux
If you want to display the biggest directories in the current working directory, run:
# du -a | sort -n -r | head -n 5
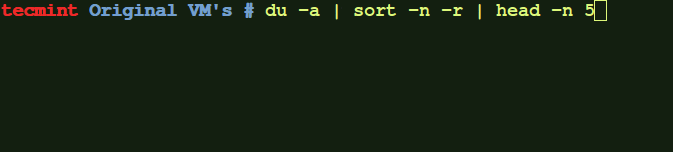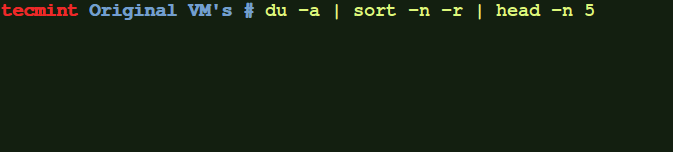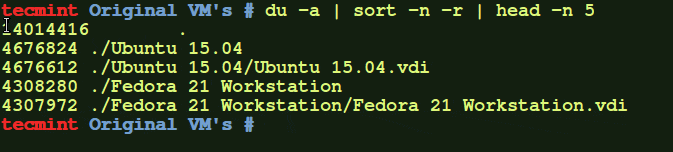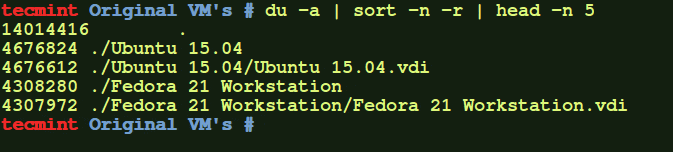
Let us break down the command and see what says each parameter.
ducommand: Estimate file space usage.a: Displays all files and folders.sortcommand : Sort lines of text files.-n: Compare according to string numerical value.-r: Reverse the result of comparisons.head: Output the first part of files.-n: Print the first ‘n’ lines. (In our case, We displayed the first 5 lines).
Some of you would like to display the above result in human-readable format. i.e you might want to display the largest files in KB, MB, or GB.
# du -hs * | sort -rh | head -5
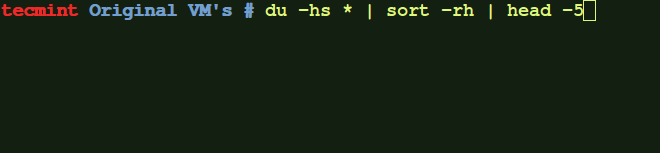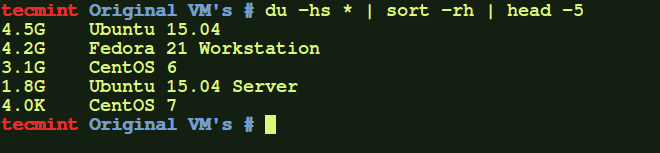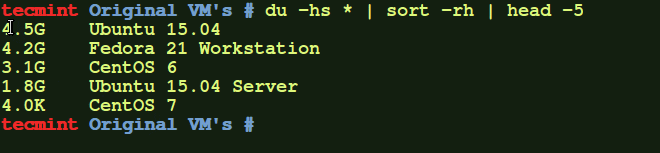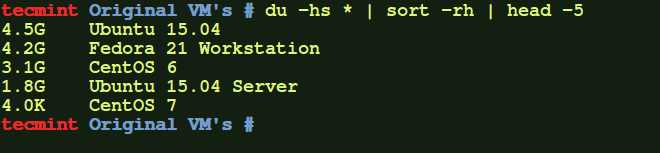
The above command will show the top directories, which are eating up more disk space. If you feel that some directories are not important, you can simply delete a few sub-directories or delete the entire folder to free up some space.
To display the largest folders/files including the sub-directories, run:
# du -Sh | sort -rh | head -5
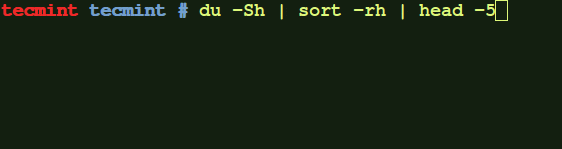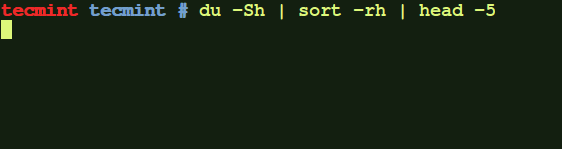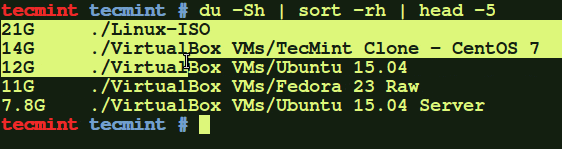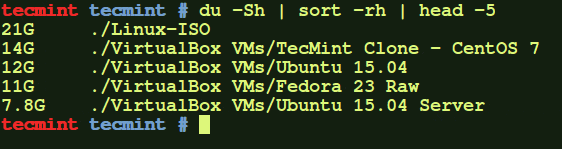
Find out the meaning of each option using in above command:
ducommand: Estimate file space usage.-h: Print sizes in human-readable format (e.g., 10MB).-S: Do not include the size of subdirectories.-s: Display only a total for each argument.sortcommand : sort lines of text files.-r: Reverse the result of comparisons.-h: Compare human readable numbers (e.g., 2K, 1G).head: Output the first part of files.
Find Out Top File Sizes Only
If you want to display the biggest file sizes only, then run the following command:
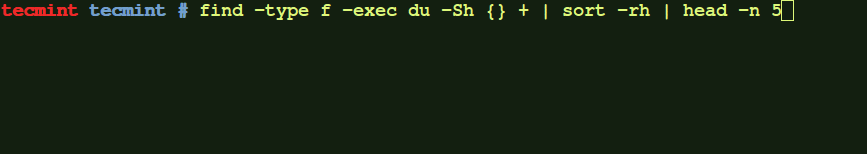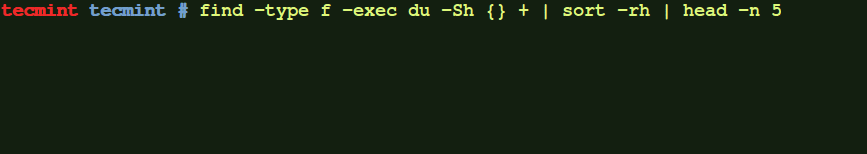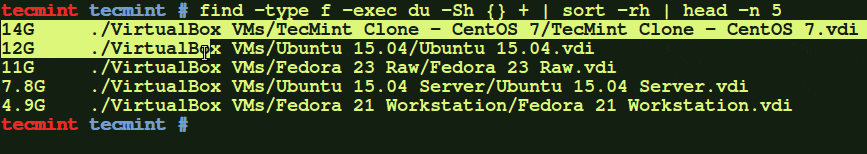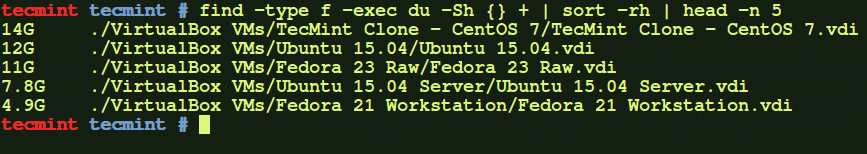
# find -type f -exec du -Sh {} + | sort -rh | head -n 5
To find the largest files in a particular location, just include the path beside the find command:
# find /home/tecmint/Downloads/ -type f -exec du -Sh {} + | sort -rh | head -n 5
OR
# find /home/tecmint/Downloads/ -type f -printf "%s %p\n" | sort -rn | head -n 5

The above command will display the largest file from /home/tecmint/Downloads directory.
That’s all for now. Finding the biggest files and folders is no big deal. Even a novice administrator can easily find them. If you find this tutorial useful, please share it on your social networks and support TecMint.
