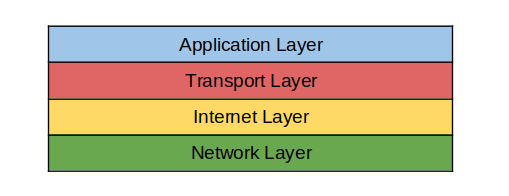
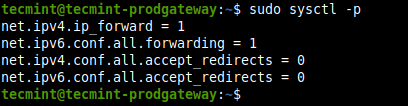
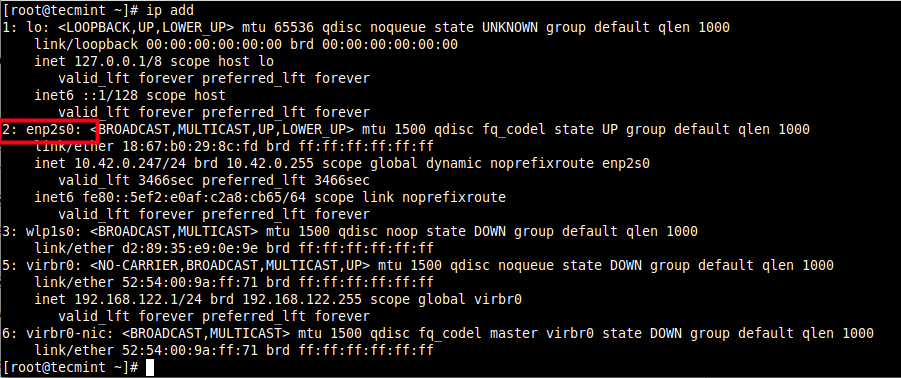
When systems encounter issues, as they sometimes will, you need to know your way around the problem and restore them back to a normal and functioning state. In this section, we focus on fundamental network troubleshooting skills that any Linux systems administrator should have. Fundamental Understanding of Network Troubleshooting In most cases, there is a
Networking Tips - DesignLinux
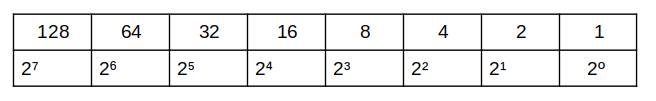
LFCA: Learn Binary and Decimal Numbers in Network – Part 10
In Part 9 of the LFCA series, we covered the basics of IP addressing. To better understand IP addressing, we need to pay more attention to these two types of IP address representation – binary and decimal-dotted quad notation. As mentioned earlier, an IP address is a 32-bit binary number that is usually represented in
How to Configure Static IP Address on Ubuntu 20.04
Usually, when a client system connects to a network via WiFi or an ethernet cable, it automatically picks an IP address from the router. This is made possible through the DHCP server which auto-assigns IP addresses to clients from a pool of addresses. The drawback with DHCP is that once the DHCP lease time has
How to Configure Network Static IP Address on RHEL/CentOS 8/7
The scope of this tutorial is to explain how we can edit and make changes to Network Configurations on RHEL/CentOS 8/7 from the command line only, and, more specifically how we can set up a Static IP address on network interfaces using system network-scripts, which is a must be configured to serve Internet-facing network services, and
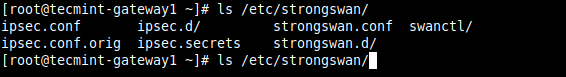
How to Set Up IPsec-based VPN with Strongswan on Debian and Ubuntu
strongSwan is an open-source, cross-platform, full-featured and widely-used IPsec-based VPN (Virtual Private Network) implementation that runs on Linux, FreeBSD, OS X, Windows, Android, and iOS. It is primarily a keying daemon that supports the Internet Key Exchange protocols (IKEv1 and IKEv2) to establish security associations (SA) between two peers. This article describes how to set
3 Ways to Create a Network Bridge in RHEL/CentOS 8
A network bridge is a data-link layer device that interconnects two or more network segments, offering communication between them. It creates a single network interface to set up a single aggregate network from multiple networks or network segments. It forwards traffic based on the MAC addresses of hosts (stored in a MAC address table). Linux
How to Set Up IPsec-based VPN with Strongswan on CentOS/RHEL 8
strongSwan is an open-source, multi-platform, modern and complete IPsec-based VPN solution for Linux that provides full support for Internet Key Exchange (both IKEv1 and IKEv2) to establish security associations (SA) between two peers. It is full-featured, modular by design and offers dozens of plugins that enhance the core functionality. Related Article: How to Set Up
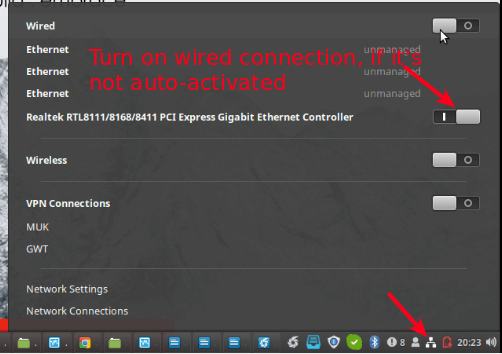
How to Share Wired Internet Via Wi-Fi and Vice Versa on Linux
In this article, you will learn how to share a wired (Ethernet) internet connection via a wireless hotspot and also how to share a wireless internet connection via a wired connection on a Linux desktop. This article requires you to have at least two computers: a Linux desktop/laptop with a wireless card and an Ethernet
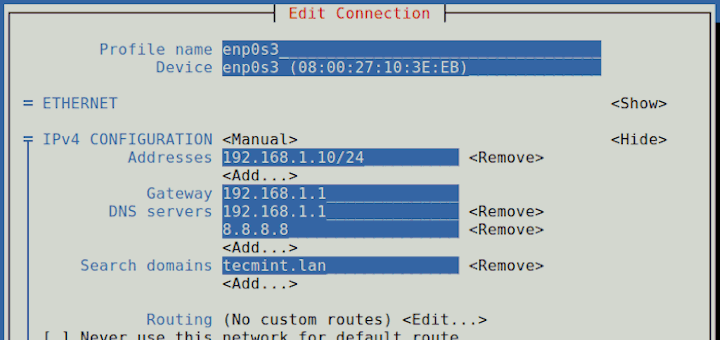
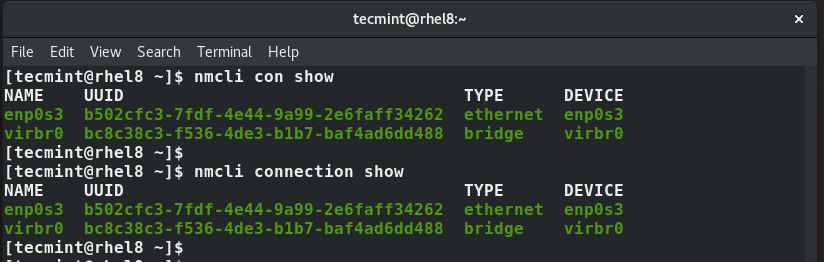
How to Configure Network Connection Using ‘nmcli’ Tool
Abbreviated as nmcli, the network manager command-line interface is a nifty and easy to use tool that saves you lots of time when you need to configure an IP address. Read Also: How to Configure IP Network with ‘nmtui’ Graphical Tool To display all the active network interfaces on your Linux system execute the command.
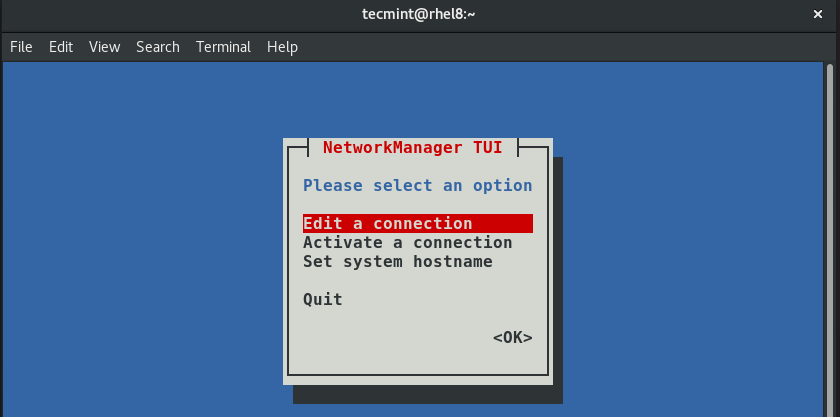
How to Configure IP Network with ‘nmtui’ Tool
An alternative for the nmcli is the nmtui, short for Network Manager Text User Interface, the nmtui is yet another handy tool that allows you to easily configure your network interfaces in Linux distributions using a graphical display by invoking the nmtui command straight from the terminal or even putty. To configure a network interface