Varnish Cache (commonly known as Varnish), is an open-source, popular reverse-proxy HTTP accelerator intended for speeding up web servers. It is engineered for excessively utilized API endpoints and also for dynamic sites that serve massive-content and experience high-traffic. For Nginx: How to Install Varnish Cache for Nginx on CentOS 7 It basically helps to scale
Varnish Cache - DesignLinux
How to Speed Up Nginx with Varnish Cache on CentOS 7
Varnish Cache (also referred to as Varnish) is an open-source, high-performance HTTP accelerator designed for speeding up web servers. In our last articles, we’ve explained how to setup Varnish Cache for Apache on CentOS 7 and CentOS 8. In this article, we will show you how to install and use Varnish Cache as a front-end
How To Install Varnish Cache 6 for Nginx on CentOS/RHEL 8
Varnish Cache (commonly referred to as Varnish) is an open-source, powerful and fast reverse-proxy HTTP accelerator with modern architecture and flexible configuration language. Being a reverse proxy simply means it is a software that you can deploy in front of your web server (which is the origin server or backend) such as Nginx, to receive
How to Install Varnish Cache for Apache on CentOS/RHEL 8
Varnish Cache is a free open source, modern and high-performance web application accelerator. It is a fast reverse HTTP proxy that caches content to speed up your web server performance, by storing web content in server memory – in a cache. It is configured to run in front of an origin server such as Apache
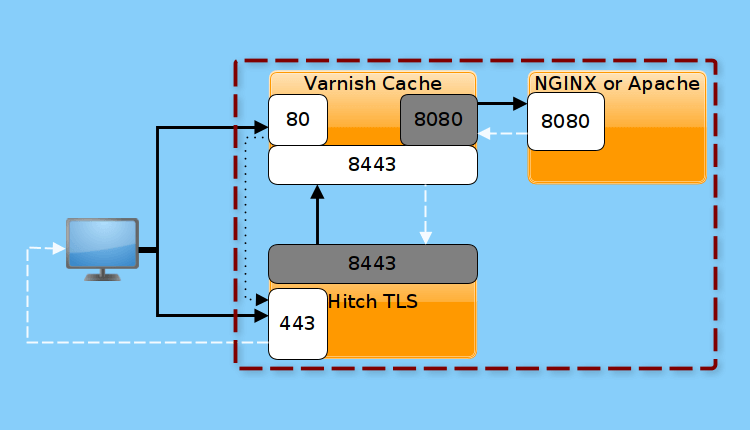
How To Enable HTTPS for Varnish Cache using Hitch on CentOS-RHEL 8
Varnish Cache lacks native support for SSL/TLS and other protocols associated with port 443. If you are using Varnish Cache to boost your web application’s performance, you need to install and configure another piece of software called an SSL/TLS termination proxy, to work alongside Varnish Cache to enable HTTPS. The Hitch is a free open